* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - Our Lady Of The Wayside School
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
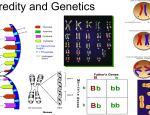
• Passing of genetic material from parent to offspring • Genetics • Study of heredity • • • • Monk Worked with pea plants Father of Genetics Studied traits • Dominant • Stronger trait • Use capital letter (example tallness T) • Recessive • • • • • Weaker trait Can disappear Smaller letter (shortness t) Every organism has 2 forms of the gene for each trait True breeding: TT (tall plant) or tt (small plant) • Genes- segments of DNA found in chromosomes for characteristic • Allele- different version of gene; get one version from each parent • Homozygous (purebred)- organism with 2 dominant or 2 recessive alleles • Hertozygous (hybrid)- organism with one dominant and one recessive allele • Genotype- combination of alleles inherited by parents • Phenotype- traits you can see • Complete dominance- one trait is completely dominant over another (you either have it or you do not) Many genes can influence a single trait • Skin, hair, and eye color are based on many alleles A single trait can influence many traits • Usually with genetic diseases • Example: sickle cell anemia is on one gene • Animals and their fur coats depend on living environment • Humans can grow tall, but need proper nutrition • Traits can also be learned: example being a good reader (acquired) • Incomplete dominance: no dominant or recessive • Example: P (parent generation) BB (brown) WW (white) F1 (first generation) BW (palomino) BW (palomino) F2 (2nd generation) BB (brown) BW (palomino) WW (white) • Codominance: both genes contribute to the phenotype, have both traits • Example: 3 blood type alleles- A, B, O • AB blood is co-dominant, get both A and B antigens • One gene from each pair goes to each sex cell Yy (parent) Y (sex cell) y (sex cell) • Female: XX • Male: XY • Each gives one chromosome • Male determines gender of child • Each gene pair for a trait is inherited independently of the gene pairs for all other traits • Example: Tall plant Tt Yellow seeds Yy