* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
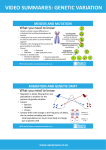
Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. You will see lots of cats monohybrid The coat colour of cats shows a large amount of discontinuous variation. This suggests that each cat’s coat colour is likely to be produced by the alleles of a large number of genes. Despite the complexity that this large number of genes causes, each one is inherited in the same way. parental phenotypes this that parental genotypes AA Aa gamete genotypes A A dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid offspring genotypes offspring phenotypes a A a A AA Aa A AA Aa ½ are this (AA) and ½ are that (Aa), the probability that it will be this is 0.5 Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. Monohybrid inheritance This is when a small number of phenotypes (usually only 2 or 3) are the result of one gene. The gene has more than one allele (often 2 but it can be more). One allele is usually dominant. This means that it is expressed whenever it is present in an individual. The other allele is recessive. It is only expressed if it is the only allele present in an individual. monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid MM or Mm mm Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. Incomplete or Co-dominance Sometimes the dominance of one allele isn’t complete. This usually results in three phenotypes produced by two alleles instead of two. Two phenotypes are produced by homozygous genotypes, the third phenotype is produced when an individual is heterozygous. The third condition is often intermediate between the other two phenotypes. ss monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid SS Ss Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. Sex linkage The locus of some genes is on the sex chromosome. The gene is only present on the X chromosome because the Y chromosome has a different structure. Females have 2 copies of these genes but males only have one since females have two X chromosomes. The ratio of males and females with particular phenotypes in a set of offspring can be unequal. monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid XOXO or XOXo or XOY XoXo or XoY Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. Multiple alleles Each gene locus can have more than 2 alleles. An allele may be dominant to some alleles but recessive to others. This situation produces more than 2 different phenotypes. Each individual has 2 alleles present in their cells at any one time. BB or Bb or Bbl monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles bb or bbl dihybrid blbl Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid Dihybrid inheritance A phenotype can be produced by the action of two (or more) genes, each with several alleles. The expression of the two pairs of alleles can interact directly or indirectly to produce the phenotype. Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid Dihybrid inheritance A phenotype could be produced by the action of two (or more) genes, each with several alleles. The expression of the two pairs of alleles can interact directly or indirectly to produce the phenotype. Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid Guess the parents! Lesson Aims You will see examples of the main ways by which features are inherited. You will record an example of each inheritance pattern including a genetic diagram. monohybrid dominance sex linkage multiple alleles dihybrid Multiple gene inheritance Cat coat colour is the result of the inheritance of a large number of different genes.