* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Previously on Bio308
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
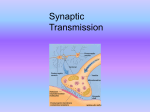
Previously on Bio308 Adapted from Fig21-2b Introduction to Bipolar Disorder Parts of a neuron Types of synapses Parts of a synapse Fig21-42 Now on Bio308 Compounds that mediate signaling Types of responses that occur Post-synaptic cell receptors Compounds that mediate signaling Neurotransmitter vs Neuropeptide vs Neurohormone? Recognize any structures? Whats a catechol? Compounds that mediate signaling Catecholamines and Bipolar disorder Catecholamine theory of affective disorder Mania and depression caused by change in The amount of activity at noradrenergic synapses Problems Use of amino acids as neurotransmitters Use of nucleotides/nucleosides as neurotransmitters Use of peptides for paracrine or endocrine signaling Why might these things pose problems? How does the body get around those problems? Ions and the cell Voltage and membrane potential Does the type of ion(s) matter? Concentration gradients and Ex Where are these ions? Post-synaptic cell Ca++ Na+ K+ Cl- To cell body Excitatory vs Inhibitory synapses What are they? How do ions play a role in these responses? What lets the ions in? The action of Receptors Adapted from fig21-38 Types of neurotransmitter receptors Types of neurotransmitter receptors Similarities? Differences? Fig 21-38b Ligand-gated ion channels Fig 21-41 G protein coupled receptors Receptors 2 types of acetylcholine receptors: same ligand different response Glutamate Non-NMDA Mg++ 2 types of glutamate receptors NMDA Na+ Na+ Removal of Mg++ Explain response Coincidence detector Na+ Ca++ Na+ Na+ Na+ Ca++ Adapted from fig 21-40 Next on Bio308 Neurotransmitters Soluble Neurotransmitter receptors Transmembrane How do they get where they need to be? Part I: soluble neuropeptide –From DNA to protein DNAtranscriptionmRNAtranslationprotein All in one day!