* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 ATP - Loyola Blakefield
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
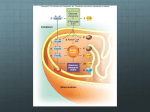
Drill 1.What are some differences between the liquids used in the investigation? 2.Using the terms isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic, explain the changes in mass of the 2 eggs. 3.Would you expect the same results if you used eggs that were still in their shells? Objectives -Introduction: Respiration -Midterms: 5 minutes Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Outline I. Cellular Respiration A. Introduction B. Reactions (Anaerobic and Aerobic) II. Photosynthesis A. Introduction B. Reactions CELLULAR RESPIRATION C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Pick a color What is ATP? -Adenosine Triphosphate -Energy used by all cells -Organic molecules containing highenergy phosphate bonds HYDROLYSIS (Adding H2O) H2 O Copyright Cmassengale Break bonds…..ENERGY! An Enzyme! Copyright Cmassengale Remaking ATP ATP Synthetasean enzyme that builds ATP from ADP Copyright Cmassengale The ADP-ATP Cycle ATP Synthetase ATP-ase Copyright Cmassengale Homework due 1/24/2012 Read pages 221-225 Complete questions on page 237: #1-6, 10, 12-15 Structure of a Mitochondria Inner membrane Outer membrane Intermembrane space Composed of folds or shelves called cristae. The electron transport chain occurs along the cristae. Gel filled space between the outer and inner membrane Matrix Gel-like fluid inside the inner membrane Cell Respiration Occurs across Cristae Occurs in Cytoplasm Occurs in Matrix Copyright Cmassengale Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasm • Begins both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. • A 10 step process. 2 ATP Glucose 2 ADP Requires an input of energy to initiate the reaction. 2 ADP NAD+ 2 molecules of G3P NAD+ 2 ATP NADH To the 2 molecules electron of pyruvate transport chain NADH 2 ATP 2 ADP Adapted from Glycolysis © Pearson Education, Inc. An overview of cellular respiration Electrons carried via NADH and FADH2 Electrons carried via NADH Glycolsis Pyruvate Glucose Cytosol ATP Figure 9.6 Substrate-level phosphorylation Citri c acid cycle Oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and chemiosmosis Mitochondrion ATP Substrate-level phosphorylation ATP Oxidative phosphorylation When you exercise, your body uses oxygen to get energy from glucose, a 6-carbon sugar 1. How does your body feel at the start of exercise, such as a long slow run? How do you feel 1 minute into the run; 10 minutes into the run? 2. What do you think is happening in your cells to cause the changes in how you feel? 3. Have you ever had a stomach cramp while exercising? Think about what was happening when that occurred. Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasm • Begins both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. • A 10 step process. 2 ATP Glucose 2 ADP Requires an input of energy to initiate the reaction. 2 ADP NADH NAD+ 2 molecules of G3P 2 ATP To the electron transport chain NAD+ NADH 2 ATP 2 ADP Adapted from Glycolysis © Pearson Education, Inc. 2 molecules of pyruvate Cellular Respiration: GLYCOLYSIS – Reactions to hydrolyze a 6-C glucose molecule into two 3-C molecules called pyruvate/pyruvic acid – All organisms from simple bacteria to humans perform it the same way – Cytoplasm & Anaerobic *Input: 2 ATP molecules *Yield: 2 ATP molecules/ glucose molecule *Yield: 2 NADH/ glucose molecule •Produces 2 NADH and 4 ATP •Pyruvate is oxidized to Acetyl CoA and CO2 is removed Anaerobic Cellular Respiration Some organisms thrive in little or no oxygen – Marshes, bogs, gut of animals, sewage treatment ponds No more ATP: final steps in these pathways serve ONLY to regenerate NAD+ so it can return to pick up more electrons and hydrogens in glycolysis. Produces: ethanol and CO2 (single cell fungi (yeast) in beer/bread) or lactic acid (muscle cells) Fermentation Occurs when O2 NOT present (anaerobic) Called Lactic Acid fermentation in muscle cells (makes muscles tired) Called Alcoholic fermentation in yeast (produces ethanol) Nets only 2 ATP Copyright Cmassengale Fermentation LAB Review Lab Procedure Pre-lab questions Lab Lab Report. http://photography.nationalgeographic.com/staticfiles/NGS/Shared/StaticFiles/Photography/Images/POD/m /micro-yeast-522314-sw.jpg WHIP AROUND Stand up with a partner, back to back, with both individuals easily viewing the board True or False Glucose and oxygen are the reactants of cellular respiration True or False Photosynthesis takes place in the mitochondrial matrix True or False Fermentation yields only 2 ATP True or False The Krebs cycle yields 2 pyruvic acid True or False Aerobic respiration is the most efficient manner of energy production 1.When ATP is recharged, that means that a ___________ is being added onto _______. 2. When ATP is spent or used, that means that a ___________ is taken off of ______ _. 3. _________can be compared to a fully-charged battery _________can be compared to a run-down battery. 4. Energy is stored for use by cells in ATP molecules. What is the source of that energy? Wednesday February 2, 2011 1) 2) 3) 4) Review and collect yeast problem Aerobic respiration-Krebs cycle Quiz: Monday HW: posted online Read pg 220-227 pg 237 q. 1-10, 12-13-14-15 Aerobic Cellular Respiration Oxygen required=aerobic 2 more sets of reactions which occur in a specialized structure within the cell called the mitochondria 1. Kreb’s Cycle 2. Electron Transport Chain Kreb’s Cycle Completes the breakdown of glucose Takes the pyruvate (3-carbons) and breaks it down, the carbon and oxygen atoms end up in CO2 and H2O Hydrogens and electrons are stripped and loaded onto NAD+ and FAD to produce NADH and FADH2 Production of only 2 more ATP but loads up the coenzymes with H+ and electrons which move to the 3rd stage Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Electron carriers loaded with electrons and protons from the Kreb’s cycle move to this chain-like a series of steps (staircase). As electrons drop down stairs, energy released to form a total of 32 ATP Oxygen waits at bottom of staircase, picks up electrons and protons and in doing so becomes water Electron Transport Figure 8.14 Electron transport occurs along the mitochondrial membrane. Energy Tally 36 ATP for aerobic vs. 2 ATP for anaerobic Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb’s 2 ATP Electron Transport 32 ATP 36 ATP Anaerobic organisms can’t be too energetic but are important for global recycling of carbon A Summary of Glycolysis Process Glycolysis Where in the cell does this process occur? Cytoplasm What are the reactants of this process? Glucose (C6H12O6) 2 ATP 4 ADP + 2 NAD 4 What are the products of this process? 2 ADP 4 ATP 4 2 NADH 2 pyruvate How many ATP are generated? Net of 2 ATP A Summary of the Krebs Cycle Process Krebs Cycle Where in the cell does this process occur? Mitochondria Matrix What are the reactants of this process? 2 pyruvate 2 ADP 2 FAD 8 NAD+ What are the products of this process? 2 ATP 8 NADH 6 CO2 2 FADH2 How many ATP are generated? 2 ATP A Summary of Electron Transport Process Electron Transport Where in the cell does this process occur? Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria What are the reactants of this process? 2 FADH2 32 ADP 10 NADH 6 O2 What are the products of this process? 32 ATP 10 NAD+ 6 H2 O 2 FAD How many ATP are generated? 32 ATP A Summary of Cellular Respiration Process Where in the cell does this process occur? Glycolysis Cytoplasm Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Mitochondrial Matrix Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria What are the reactants of this process? What are the products of this process? Glucose 2 ADP 2 NAD++ 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 pyruvate 2 pyruvate 2 ADP 2 FAD + 8 NAD+ 2 ATP 8 NADH 6 CO2 2 FADH2 2 FADH2 32 ADP 10 NADH 6 O2 32 ATP 10 NAD+ 6 H2O 2 FAD How many ATP are generated?