* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio102A organic notes (2)
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
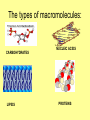
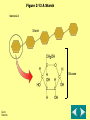
•Biology 102A Organic Chemistry Notes Journal 4 • Complete the Venn diagram below: Acids 1 1 2 1 2 Bases What is organic chemistry? The study of all compounds containing the element CARBON Natural elements: make up 96% of the mass of a human: CARBON, HYDROGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN (CHON) Trace elements: only needed in small amounts, called “minerals”: What is a macromolecule? A giant molecule made up of 100’s or 1000’s or smaller units called MONOMERS Monomers link together to form large POLYMERS formed by polymerization The types of macromolecules: CARBOHYDRATES LIPIDS NUCLEIC ACIDS PROTEINS CARBOHYDRATES Made up of C,H,O Used as main source of energy Sugars: quick source of energy Monosaccharide-simple sugar, disaccharide-2, polysaccharide-many Two types: Ex: glucose, lactose, fructose, sucrose Starches: many sugars linked together, source of energy breaking down slower Used by plants for energy storage Ex: potatoes, pasta, bread, grains Figure 2-13 A Starch Section 2-3 Starch Glucose Go to Section: LIPIDS Made up mainly of C & H Used to store energy, insulation & protection Usually not soluble in water Saturated: has maximum number of H bonds, usually solid at room temperature Unsaturated: at least one double bond, causes “kinks”, usually liquid PROTEINS Made up of N,C,H, O Made up of groups called amino acids (20 in nature) proteins have a large variety of sizes & shapes If the shape changes, it becomes a new protein Ex: when you boil an egg, the protein changes color, shapej Found in muscles, cellmembrane Nucleic Acids Made up of H,O,N,C & P Store and transmit genetic information Made up of nucleotides Two types: DNA & RNA Reinforcement 1. All organic compounds contain which element? a. calcium b. carbon c. chlorine 2. Is water an organic compound? a. yes b. no c. sometimes it is and sometimes not 3. Which macromolecule is made up of amino acids? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. proteins 4. Starches & sugars are both examples of which macromolecules? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. proteins 5. Fats & oils are both examples of which macromolecule? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. proteins