* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.2 Carbon compounds and cells
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
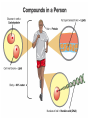
4.2 Carbon compounds and cells • Life as we know it is carbon based. • A carbon atom can form chemical bonds with other carbon atoms in long chains or rings. 4.2 Carbohydrates, fats and proteins • Carbohydrates are energy-rich compounds made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. • Cells use carbohydrates to get and store energy. • Carbohydrates are also called sugars or starches. 4.2 Carbohydrates • Plant cells store energy as starch. • Rice, potatoes, and wheat are plant starches. 4.2 Lipids • Lipids are made by cells to store energy for long periods of time. • Lipids include fats, oils, and waxes. Can you think of examples of lipids in plants or animals? 4.2 Proteins • Proteins are very large molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. • Protein molecules are made of smaller molecules called amino acids. 4.2 Nucleic acids • Nucleic acids are compounds made of long, repeating chains called nucleotides. • DNA is a nucleic acid that contains the information cells need to make all of their proteins.