* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aminosav metabolizmus IV. Aminosavak bioszintézise
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
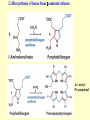
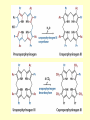
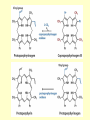
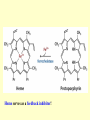
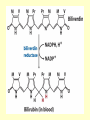
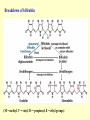
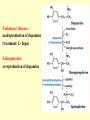
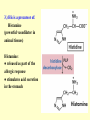
Amino acid metabolism IV. Synthesis of biologically active molecules from amino acids Figures: Lehninger-4ed; chapter: 22 (Stryer-5ed; chapter: 24) Glycine: precursor of porphyrins in mammals 1.) Biosynthetic pathways of -aminolevulinate 2.) Biosynthesis of heme from -aminolevulinate Ac: acetyl Pr: propionyl Heme serves as a feedback inhibitor! Porphyrias: group of genetic diseases caused by the accumulation in body fluids, and liver of some porphyrin precursors (because of the defect of certain enzyme in the biosynthesis of porphyrin). ● buildup of -aminolevulinate and porphobilinogen (acute intermittent porphyria) - acute abdominal pain - neurological disfunctions (apparent madness) ● accumulation of uroporphyrinogen (rare) - red urine, the teeth fluoresce in UV light - very sensitive skin to sunlight - anemia (insufficient heme) vampire miths? 3.) Heme as the source of bile pigments (heme released from dying erythrocytes in the spleen is degraded) Fe2+ binds to ferritin, CO (poison) binds to hemoglobin (1%) Breakdown of bilirubin (M = methyl, V = vinyl, Pr = propionyl, E = ethyl groups) Hemoglobin released from damaged erythrocytes: black/purple Biliverdin: green Bilirubin: yellow Urobilin: gives the yellow colour to the urine Stercobilin: gives the red-brown colour to feces Jaundice: yellow skin and eyeballs (due to impaired liver function or blocked bile secretion bilirubin leaks into the blood) Jaundice in newborn infants: not enough glucuronyl bilirubin transferase (exposure to fluorescent lamp photochemical conversion of bilirubin) These pathways of heme degradation: ● protect cells from oxidative damage ● regulate certain cellular functions CO produced by HO: ● toxic (high conc.) ● vasodilator as NO (low conc.) ● regulatory effects on neurotransmission (low conc.) Bilirubin: ● the most abundant antioxidant in mammalian tissues (antioxidant activity in serum) ● protective effect in developing brain of the newborns Gly and Arg: precursors of creatine Phosphocreatine is an important energy reservoir in skeletal muscle it can rapidly regenerate ATP from ADP by creatine kinase reaction. active contraction and glycolysis ATP synthesis light activity/rest phosphocreatine synthesis at the expense of ATP Gly, Glu and Cys: precursors of glutathione (GSH) (disulfide bond) GSH (redox buffer): ● maintain the -SH groups of proteins in the reduced form ● the iron of heme in ferrous state (Fe2+) ● serves as reducing agent for glutaredoxin (deoxyribonucleotide synth.) ●removes toxic peroxides formed during growth and aerobic metabolism 2GSH + R–O –O –H GSSG + H2O + R –OH (glutathione peroxidase: contains selenocystein!) Aromatic amino acids: precursors of many plant substances Phe, Tyr ↓ tannins, alkaloids (morphine), cinnamate, nutmeg, cloves, vanilla, cayenne pepper, etc. Plant growth hormone Biosynthesis of some neurotransmitters from amino acids 1.) Tyr is a precursor of catecholamines: • Dopa • Dopamine • Norepinephrine • Epinephrine Levels of catecholamines are correlated with changes in blood pressure! Parkinson’s disease: underproduction of dopamine (treatment: L- dopa) Schizophrenia: overproduction of dopamine 2.) Glu is a precursor of: GABA (inhibitory neurotransmitter) Epileptic seizures: underproduction of GABA GABA analogs: treatment of epilepsy and hypertension 3.) His is a precursor of: Histamine (powerful vasodilator in animal tissues) Histamine: ● released as part of the allergic response ● stimulates acid secretion in the stomach 4.) Trp is a precursor of: Serotonin (imp. neurotransmitter) 5.) Met is a precursor of: spermine and spermidine (polyamines involved in DNA packaging) Biosynthesis of nitric oxide (NO) from Arg (nitric oxide synthase reaction) NO synthase : dimeric enzyme, structurally related to NADPH cytochrome P-450 reductase NO: important biological messenger ● neurotransmission ● blood clotting ● controling blood pressure