* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NS 315 Unit 6: Proteins
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
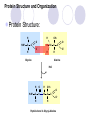
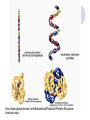
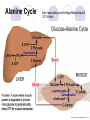
NS 315 Unit 6: Proteins Jeanette Andrade MS,RD,LDN,CDE Kaplan University Objectives Definitions Essential Amino Acids Protein Structure and Organization Protein Digestion, Absorption and Metabolism Urea Cycle Alanine Cycle Recommended Daily Intakes Case Study Defintions Amino Acids: molecule containing both amine and carboxyl functional groups Side chain Amino group Carboxylic acid group R O H2N C C OH H Protein: Large organic compounds made of amino acids arranged in a linear chain and joined together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent amino acid groups Definitions Protein Quality: Particular protein providing a balanced pattern of indispensable amino acids Denaturation: Precipitation of proteins with heat causing them to turn “inside out” Amino-transferases: enzymes transferring amino groups usually between amino group to 2-keto acid, e.g. l-alanine and 2-ketoglutarate Essential Amino Acids 9 essential amino acids we need to consume due to cannot be synthesized Acronym: PVT TIM HLL phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, histidine, leucine, and lysine http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Essential_amino_acids Protein Structure and Organization Protein Structure: H H CH3 O + H3N C O C H + N C C - O- O H H H Glycine Alanine H2O H O H CH3 O + H3N C C N C C O- H H Peptide bond in Glycyl-Alanine http://www.gbiosciences.com/EducationalProducts/Protein-StructureAnalysis.aspx Protein Digestion and Absorption Where does Protein Digestion begin? What aids in breaking down the protein structure? How are proteins absorbed into the intestinal cells? Urea Cycle: Protein Catabolism Urea is the end product of the nitrogen metabolism Ammonia must be removed from the body and usually is converted to urea to be excreted Ammonia is usually the from of energy produced during starvation mode and urea is the form of energy produced during fed states This reaction occurs in the liver and then urea is transported to the kidney Urea is generally measured in the body as BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) If BUN elevated: maybe due to renal failure, dehydration, CHF (congestive heart failure) Uric acid salts deposited within the joints can lead to a condition referred to as gout http://guweb2.gonzaga.edu/faculty/cronk/biochem/images/urea-cycle-eqn.gif Alanine Cycle Alanine is usually produced during times of exercise when oxygen depleted (anaerobic). Shuttled to liver to produce glucose Energy by-product: urea Recycles carbon skeletons between muscle and liver Transports Ammonia (NH4+) to liver to be converted to urea During liver diseases (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, cirrhosis) cannot convert NH4+ to urea http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alanine_cycle Alanine Cycle http://www.wiley.com/college/fob/quiz/quiz2 1/21-6.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alanine_cycle Recommended Daily Intake Nitrogen Balance: Difference between the amount of nitrogen consumed per day by the amount of nitrogen excreted per day Nitrogen Balance= (grams of nitrogen eaten - grams of nitrogen lost) Positive nitrogen balance indicates growth- What age groups are in the positive nitrogen balance? Protein- Case Study R.C. is a 30 year old male who is interested in losing weight and has heard the quickest way to do it is by a low carbohydrate, high protein diet. He realizes he also has to exercise, but since he cannot do cardio because he is always short of breath, he is going to lift weights. He informs you he has started incorporating more protein already into his diet and has lost 20 lbs within 2 months. When you review his diet, he is consuming 300 gm of protein per day. Height: 5’11” Weight: 330 lbs previous weight: 350 lbs (2 months ago) What do you foresee to be a problem with the amount of protein consumed? What can you suggest to this client to reduce the amount of protein consumed?