* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Code Notes
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
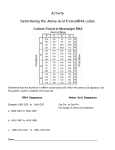
The Genetic Code Objective: F2 - Explain … process of transcription & translation …, describe the role of DNA & RNA during protein synthesis, & recognize that gene expression is a regulated process Using the Genetic Code A. Codon – 3 nitrogen bases of mRNA in a row that code for a specific amino acid B. Genetic code – a chart that shows the amino acids that correspond to the codons of mRNA C. How nucleotides are read – 3 at 1. 3 DNA nucleotides = 2. 3 mRNA nucleotides = 3. tRNA nucleotides = one time CAT GUA CAU D. Reading the Genetic Code 1. 1st letter (base) of the codon = G 2. 2nd letter (base) of the codon = U 3. 3rd letter (base) of the codon = A Using the genetic code on the front, which amino acid does the above codon produce? ________ Valine E. To “make” a protein 1. Transcribe the given DNA strand into mRNA 2. Look up the mRNA codons on the Genetic Code table Practice: DNA sequence TAC AAA GTA TGG GGC ATC 1. Transcribe into mRNA 2. Translate into an amino acid sequence AUG UUU CAU ACC CCG UAG Met- Phe- His- Thr- Pro- stop DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid 4. ACC UGG ACC Tryptophan (TRP) 5. AGA UCU AGA Serine 6. TTT AAA UUU Lysine 7. ACT UGA ACU Stop Although there are only 20 amino acids in the human body, thousands of proteins exist because the sequence and number of amino acids are different.