* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint - University of British Columbia
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Exome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
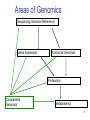
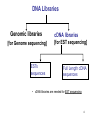
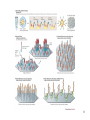
Genomics 1 Genomics relies on high-throughput technologies • Automated sequencers • Robotics – Colony pickers and Arrayers for sequencing – Microarray spotters – Protein Spot-Picker and In-gel proteolytic digestion • High-throughput genetics 2 Areas of Genomics Sequencing Genome (Reference) Gene Expression Functional Genomics Proteomics Comparative Genomics Metabolomics 3 DNA Libraries Genomic libraries [for Genome sequencing] ESTs sequences cDNA libraries [for EST sequencing] Full Length cDNA sequences • cDNA libraries are needed for EST sequencing 4 EST Library • Expressed Sequence Tags • Specific tissues and developmental stages = mRNA isolation (Conversion to cDNA) • Require cloning of cDNAs • Require many different tissues = good coverage of genomic information • Usually sequence from 5’ or 3’ end (known as pair end or mate end sequencing) • Will require more $$ to sequence both ends • Usually less than 60% of genes coverage • Will not have regulatory elements information • Paralogs issue when figuring out the annotation and function of the gene 5 FL cDNA Library • Full Length cDNA library • Require intact length of mRNA • Sequencing from both ends of the cDNA clone using the vector sequences • Clone size selection (>800 bases) • Require finishing of the larger clones by designing more primers internal to clone insert • Should translate to a full protein • Require more $$$ and effort to have the data 6 Next Generation(NG) Sequencing • Sanger sequencing for the past 25 years • Expensive, little coverage, limited nucleotide (nt) per run • Ngseq (NG 2nd) has greatly reduced cost per amount of data generated, greater coverage • Different technologies pending on company producing the technology (Metzker 2010 Nature Reviews/Genetics) 7 8 9 Next Generation(NG) Sequencing • NGseq (NG 3rd) has greatly reduced cost per amount of data generated, greater coverage • Much longer reads vs NG 2nd generation • Different technologies pending on company producing the technology (Metzker 2010 Nature Reviews/Genetics) • Ion Torrent, PacBio, Oxford Nanopore 10 PacBio NG 3rd 11 Genome Annotation Requiring Bioinformatics • Ref = Koonin, E.V. and Galperin, M.Y. 2004 In: Sequence-Evolution-Function. p.196 12 Bioinformatics • Biology, computer science, and information technology merge = a single discipline • Creating and maintaining databases to store biological information eg. nucleotide, amino acid sequences • Development of complex interfaces whereby researchers could both access existing data as well as submit new or revised data • Develop a comprehensive picture of normal cellular activities • Involves analysis and interpretation of various types of data, including nucleotide and amino acid sequences, protein domains, and protein structures 13