* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
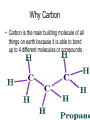
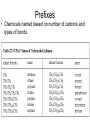
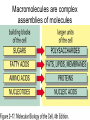
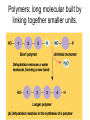
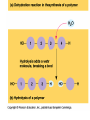
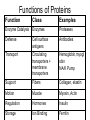
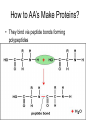
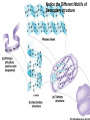
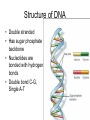
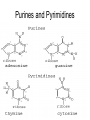
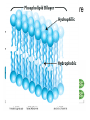
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Why Carbon • Carbon is the main building molecule of all things on earth because it is able to bond up to 4 different molecules or compounds Prefixes • Chemicals named based on number of carbons and types of bonds. Macromolecules are complex assemblies of molecules Polymers: long molecular built by linking together smaller units. How do we break bonds? Functions of Proteins Function Class Examples Enzyme Catalysis Enzymes Proteases Defense Cell surface antigens Antibodies Transport Circulating transporters + membrane transporters Hemoglobin,myogl obin NA/K Pump Support Fibers Collagen, elastin Motion Muscle Myosin, Actin Regulation Hormones Insulin Storage Ion Binding Ferritin Amino Acids: The building blocks of proteins Each Amino Acids Properties are Determined by it’s side group • 1. Nonpolar amino acids have R groups that contain CH2 or CH3 • 2. Polar uncharged AA’s have R goups that contain oxygen or only H • 3. Charged AA’s have R goups that contain acids or bases ex HCL or NAOH • 4. Aromatic AA’s have R groups that contain an organic carbon ring • 5. Special Function AA’s Methionin- start codon proline- causes kinks, cysteine links chains together. How to AA’s Make Proteins? • They bind via peptide bonds forming polypeptides Notice the Different Motifs of Secondary structure Four Levels of Protein Structure 5 types of bonds that contribute to protein shape • • • • • 1. Hydrogen bonds- O-H 2. Disulfide Bridges S-S 3. Ionic Bonds- Based on Chare 4. Vanderwalls- weak attraction 5. Hydrophobic interactions Chaperone proteins also help in protein folding How Proteins Unfold • When bonds are broken proteins will unfold – Caused by: » High Temperature » Change in pH » Enzymes my cause denaturatuin • Denaturation vs Dissacociaion- not the same thing! Nucleic acids store and transfer genetic information • DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid stores genetic info • RNA- ribonucleic acid important in transcription – 3 main differences • DNA is double stranded while RNA is single stranded • DNA has deoxyribose as the sugar whereas RNA has ribose • RNA has the nucleotide Uracil in place of Thymine Structure of DNA • Double stranded • Has sugar phosphate backbone • Nucleotides are bonded with hydrogen bonds • Double bond C-G, Single A-T Purines and Pyrimidines What came first? • DNA is thought to have evolved from RNA in order to protect and preserve genetic information Lipids Make Membranes and Store Energy • Good for long term energy storage. • Hydrophobic/hydrophi lic interactions make bilipid layered membrane Good Fats vs Bad Fats • Saturated- has max number of possible Hydrogen atoms- no double bonds ex butter • Unsaturated- has double bonds ex veggie oil • Polyunsaturated- has more than one double bond Carbohydrates: Short term energy storage and building materials • General Formula for a carbohydrate is CH2O • Monosacharides- simple sugars ex, glucose, fructose, galactose, ribose, deoxyribose • Disacharides- 2 monosacharides joined by a covalent bond- dex maltose ( glucose+glucose) • Polysacharides- more than 2 monosacharides joined together. Sugar Isomers • An isomer has the same empirical formula but different structural forms. Transport • Most of the sugar we eat are disacharides. Why? • This allows for better transport • Less of the important monosacharide is lost in transport when it is joined to another sugar. In our case we get the most glucose possible when it is paired with another sugar. Storage Polysacharides • Plants store energy in starches • Animals store energy in glycogen Structural Carbohydrates • Cellulose- found in the cell walls of plants • Chitin- found in the shells of many arthropods • These types of carbohydrates are not easily digested.