* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anaerobic Respiration - University of Indianapolis
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
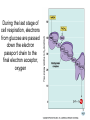
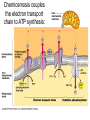
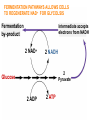
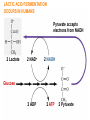
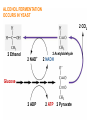
Anaerobic Respiration During the last stage of cell respiration, electrons from glucose are passed down the electron passport chain to the final electron acceptor, oxygen Chemiosmosis couples the electron transport chain to ATP synthesis: Aerobic Respiration • When oxygen is the final electron acceptor, the process is called aerobic respiration • Aerobic = occurring in the presence of oxygen Anaerobic Respiration • Some prokaryotes are able to carry out anaerobic respiration, respiration in which an inorganic molecule other than oxygen (O2) is the final electron acceptor. • For example, some bacteria, called nitrate reducers, can transfer electrons to nitrate (NO3-) reducing it to nitrite (NO2-). • Less efficient: usually 30-34 ATPs per glucose molecule. What happens if there is no available electron acceptor? Glucose 2 ADP glycolysis 2 ATP 2 NAD+ 2 NADH 2 pyruvate Aerobic respiration: The NADH then passes its high energy e- to the electron transport chain (becoming NAD+ again) and eventually to O2 Anaerobic respiration: Without O2, NADH has nowhere to donate its eto, NAD+ cannot be regenerated, and glycolysis stops Anaerobic fermentation • Fermentation: An alternative set of reactions that can follow glycolysis in the absence of oxygen as a final electron acceptor. • Extremely inefficient: no Kreb’s cycle, no ETC. Glycolysis produces a net of 2 ATP’s per glucose molecule FERMENTATION PATHWAYS ALLOWS CELLS TO REGENERATE NAD+ FOR GLYCOLSIS Fermentation by-product Intermediate accepts electrons from NADH 2 NAD+ 2 NADH 2 Pyruvate Glucose 2 ADP 2 ATP LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION OCCURS IN HUMANS Pyruvate accepts electrons from NADH 2 Lactate 2 NAD+ 2 NADH 2 ADP 2 ATP Glucose 2 Pyruvate During heavy exercise, ATP production will switch from aerobic respiration to anerobic respiration ALCOHOL FERMENTATION OCCURS IN YEAST 2 CO2 2 Ethanol 2 Acetylaldehyde 2 NAD+ 2 NADH Glucose 2 ADP 2 ATP 2 Pyruvate The Stuff of Life