* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription - Winston Knoll Collegiate
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
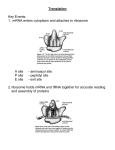
Translation From mRNA to Protein Translation Overview Genetic Code = triplets in DNA=the amino acids in proteins There are twenty different amino acids that build proteins There are 64 different triplets/codons Each amino acid is coded for by more than one triplet/codon Translation-Overview The Players mRNA:messenger RNA - carries protein recipe from the nucleus tRNA: transfer RNA -brings amino acids to the ribosome Ribosome: the site of protein synthesis - made of rRNA (ribosomal RNA )and Protein The Process of Translation mRNA takes recipe to the ribosome in cytoplasm ribosome attaches to the mRNA Translation The ribosome moves along the mRNA until it reaches the “Start” codon Start codon = AUG signals the start of the recipe AUG also codes for the amino acid methionine The process of Translation cont. •A molecule of transfer RNA brings the amino acid called for by the mRNA to the ribosome •transfer RNA = tRNA The process of Translation cont. A second tRNA bringsthe second amino acid to the ribosome The amino acids are joined together to begin the protein The process of Translation concluded The ribosome moves over 1 codon and another tRNA molecule brings another amino acid The process continues until the stop codon on the mRNA is reached -the stop codon = the end of the protein recipe Meet tRNA each molecule of tRNA carries a specific type of amino acid - each tRNA molecule can only carry one type of amino acid The tRNA has a group of 3 nucleotides at the base called the anticodon How does tRNA know which amino acid goes where? The anticodon on tRNA is complementary to a mRNA codon the amino acid that a tRNA molecule carries is the amino acid that the complementary mRNA codon codes for Example: mRNA codon = GAC = aspartic acid tRNA anticodon = CUG carries only aspartic acid What’s What? Making the building(protein) Vocabulary tRNA Triplet Codon Anticodon Start codon Stop codon