* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle Control - Georgia Institute of Technology
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
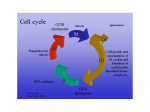
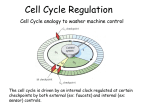
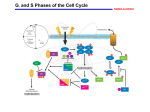
DNA Replication • • • • • • • ORC anneals to origin ORC recruits MCM MCM recruits Cdc45p Cdc45p recruits pola/primase complex RFC displaces pola and recruits PCNA PCNA recruits pold DNA ligase stitches DNA fragments together Regulation of replication • Once and only once – Licensing – DNA damage • Coordinated with cell cycle – Cyclin – Cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) – Cyclin kinase inhibitor (CKI) Key regulatory proteins • • • • • cdc6/cdt1: licensing agents E2F/DP1: S-phase transcription factor Retinoblastoma: E2F repressor p27/p21 KIP: cyclin kinase inhibitors p53: cell cycle withdrawal transcription factor Cell Cycle • G0 – Terminal differentiation • G1 • S – Replication • G2 • M – Division Cell cycle control • Cyclins – Cell cycle regulated proteins • Cyclin dependent kinases (CDK) – Signaling effectors • Cyclin kinase inhibitors (CKI) Checkpoint regulation • Phase progression tied to successful completion of prior phase – ALL DNA healthy – ALL DNA replicated – ALL DNA attached to mitotic spindles • Negative/inhibitory regulation – Signal-to-noise – Presence of “No-Go” signal – Threshold of “Ready” signal Assembly of preRC • ORC, cdc6/cdt1, MCM • Immediately following mitosis • cdt1 – Recruits MCM – Inhibited by geminin • cdc6 – Inhibits MCM helicase – Phosphorylated by CyclinA/CDK2 in S – Translocates to cytoplasm Initiation of replication • Cyclin A/cdk2 • Releases ORC inhibition • Prevents ORC Re-reformation cdt1 CyA CDK2 cdt1 ORC MCM cdc6 cdc45 ORC MCM cdc6 Licensing • ORC+cdc6 is required to recruit MCM • ORC-cdc6 is required to activate MCM • Cdc6/Cdt1 “licenses” an ORC for replication Licensing agents • Geminin – cdt1 binding protein – Cell cycle dependent expression • cdt1 – Inhibited by geminin – Stabilized by geminin – Phosphorylated by CyclinA/CDK2 in S – Phospho-form is exported & degraded – Removal allows binding of cdc45 DNA Damage • • • • Base mismatches Single strand breaks Double strand breaks Oxidation/nitrosylation Strand Break • Non-homologous end joining – Ku mediated recognition of ssDNA – End-to-end repair • Homologous recombination – Rad51 mediated search for homologous template – Template derived patch NHEJ Ku Rad51 HR Strand Break • ATM kinase recruited to strand break – Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated kinase – Autophosphorylates – Phosphorylates H2A – Phosphorylates p53 • p53 – Stabilized and activated by phosphorylation – Activates p21waf/cip (cdk inhibitor) – Blocks transcription of Pold – Blocks transcription of CyclinA Determination to divide • • • • Integrative Environmental cues Systemic/hormonal controls Internal program G1 progression • E2F/DP1 transcription factor – DNA polymerase – Cyclins A & E – CDK1 • Retinoblastoma (Rb) – De-phosphorylation dependent E2F binding – Represses E2F/DP1 – Protoconogene • P53 transcription factor – p21 CKI, MDM2 G1 progression • Growth factors cause Rb phosphorylation, which gets degraded, allowing xscription of S-phase proteins • Cdk4/CyD phosphorylates Rb… • Cdk2/CyE phosphorylate RB…. • Cdk2/CyE inhibit p27kip, which inhibits cdk2 • ATM activates p53, which leads to transcription of CKIs p21 & p27 p53/Rb • Active inhibition of cell cycle Phosphorylates to block binding Cyclin D CDK 4/6 Mitogens Rb Promotes transcription Cyclin A/E E2F Binds to block transcriptional activity Pol a CDK1 Promotes transcription Inhibits activity Phosphorylates to stabilize & p53 p21CIP/WAF CDK2/4/6 activate DNA Damage ATM kinase cdc14 phosphatase Dephosphorylates to destabilize & inactivate S-Phase Cycle Progression Regulatory features • CDKs regulate cell cycle – Phase specific transcription – Cyclin E/cdk2 promotes Cdc6 transcription – Cyclin A/CDK2 activates synthesis – Cyclin B/cdc2 deactivate Mcm • Rb keeps the gate at G1 restriction – Represses CDK2 & polymerase expression • p53 blocks cell cycle & promotes apoptosis – Promotes expression of CKIs Controls on DNA replication • Growth factors/mitogens – Rb phosphorylation – Cyclin D upregulation • Nutrient availability – Cell size – amino acids, PO4 – GSK inactivates cyclinD • Stress states – DNA damage – ATM phosphorylates p53CKI expression