* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 呼吸系统用药(汤慧芳2015V2)
Orphan drug wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Psychedelic therapy wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
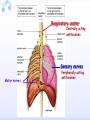
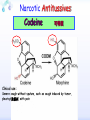
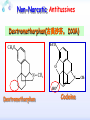
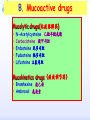
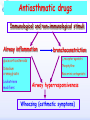
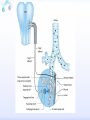
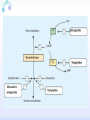
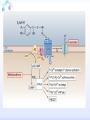
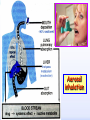
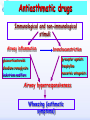
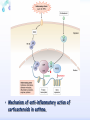
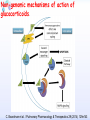
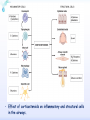
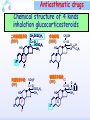
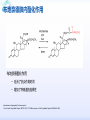
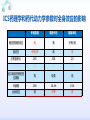
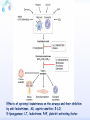
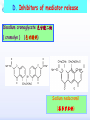
Drugs for treatment of respiratory diseases Huifang Tang Department of pharmacology Zhejiang University, school of medicine [email protected] Research building C422 Various diseases of respiratory system Common symptoms: cough sputum wheezing Classification of drugs acting on respiratory system Ⅰ. Antitussive drugs: 1. Centrally acting: Codeine 2. Peripherally acting: Benzonatate Ⅱ. Expectorant drugs: 1. Sputum-diluting drugs: NH4Cl、KI 2. Mucolytic drugs: Ambroxol Ⅲ. Antiasthmatic drugs: 1. Bronchial dilators (1) receptor agonists: Salbuterol (2)theophyllines: Aminophylline (3)muscarinic antagonists: Ipratropine 2. Anti-inflammatory drugs (1)glucocorticosteroids: Budesonide (2)mediator release inhibitors: Disodium cromoglycate A. Antitussives 物理、 化学 刺激 感受器(刺激感受器、牵张感 受器等) 传入神经(迷走、喉上神经) 咳嗽中枢(延髓) 传出神经(迷走、喉返、膈神经) 效应器(声门、 呼气肌) 咳嗽反射示意图 咳嗽反射 Respiratory center Centrally acting antitussives Sensory nerves Motor nerves Peripherally acting antitussives A. Antitussives Central antitussives Narcotic drugs: codeine 可待因 pholcodine 福尔可定 Drotebanol 羟蒂巴酚 Non-Narcotic drugs: dextromethorphan 右美沙芬 pentoxyverine 喷托维林(咳必清) Peripheral antitussives benzonatate 苯佐那酯 Narcotic Antitussives Codeine Clinical use: 可待因 Severe cough without sputum, such as cough induced by tumor, pleurisy(胸膜炎) with pain Narcotic Antitussives Name morphine cough suppressant effects 4 analgesic effects dependence 10 10 Codeine (可待因) 1 1 1 Dihydrocodeine (双氢可待因) 1.5 1.5 0 Drotebanol(羟蒂巴酚) 10 <10 Pholcodine(福尔可定) Clinical use: Severe cough without sputum 0 less Non-Narcotic Antitussives Dextromethorphan(右美沙芬, DXM) H3CO O N HO Dextromethorphan Codeine CH 3 Non-Narcotic Antitussives Dextromethorphan • Mechanism of action nonselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sigma-1 receptor agonist Major metabolite dextrorphan(右啡烷) as an NMDA receptor antagonist, producing effects similar to ketamine and phencyclidine (PCP,苯环利啶,俗称天使尘), Active metabolite 3-methoxymorphinan, which produces local anesthetic effects in rats with a potency above dextrorphan but below dextromethorphan itself. Non-Narcotic Antitussives (1)Pharmacological effects: Depression of coughing center; (2)Clinical uses: Upper respiratory infection and dry cough. (3)Adverse reaction: Atropine-like side effects. Contraindication: In the patients with glaucoma, pregnancy(< 3 months), psychotic disorders, etc. Non-Narcotic Antitussives Pentoxyverine(喷托维林, 咳必清) (1)Pharmacological effects: Depression of coughing center, Local anesthetic effects, and Muscarinic antagonism. (2)Clinical uses: Upper respiratory infection, Cough without sputum. (3)Adverse reaction: Atropine-like side effects. • Uses and adverse effects are similar to dextromethorphan Others Non-Narcotic Antitussives Pharmacological effects Cloperastine (氯哌斯汀) Promolate(普 罗吗酯) Fominoben (福米诺苯) Zipeprol (齐培丙醇) Side effects a mild bronchorelaxant antihistaminic activity acting on the central nervous system or the respiratory center Sedative effect bronchorelaxant effect Depression of coughing center Depression of coughing center Act on respiratory center a local anaesthetic mucolytic antihistamine properties anticholinergic properties hallucinations (幻觉) A. Antitussives • Peripheral antitussives • Benzonatate 苯佐那酯 (退嗽) • • • Blocking cough reflex Local anesthetic effects CNS depression • Others: – Benproperine(苯丙哌林) – Dropropizine (羟丙哌嗪) – Noscapine (那可汀); moguisteine (莫吉司坦) – Prenoxdiazine (普诺地嗪) – Dioxopromethazine (二氧丙嗪) Peripheral Antitussives Pharmacological effects antitussive activity side effects 1 constipation or respiratory depression Codein central action Benproperine (苯丙哌林) peripheral and central action 1 Levodropropizine (左羟丙哌嗪) a peripheral action, without action in the central nervous system sigma receptor agonist similar to dextromethorphan Narcodine (那可丁) Moguisteine (莫吉司坦) novel peripheral action less less 常用镇咳药比较表 药物 药效 镇痛 解痉 成瘾性 可待因 1 右美沙芬 1 喷托维林 1/3 + + 临床应用 剧烈干咳,尤适 用于胸膜炎干咳 伴胸痛者 干咳 + 上呼吸道炎症引 起的干咳 尤适用于小儿百 日咳 苯丙哌林 3 + 刺激性干咳 B. Mucoactive drugs Hydration: Sputum dilution Mucolysis Mucous glycoprotein network B. Mucoactive drugs Expectorants (Stimulating bronchial secretion 痰液稀释药) Ammonium chloride 氯化铵 Glyceryl guaiacolate (Guaifenesin )愈创木酚 甘油醚 Potassium iodide 碘化钾 Ipecac syrup 吐根糖浆 酒石酸锑钾、桔梗、远志等。 B. Mucoactive drugs Mucolytic drugs(粘痰溶解药) N-Acetylcysteine 乙酰半胱氨酸 Carbocisteine 羧甲司坦 Erdosteine 厄多司坦 Fudosteine 福多司坦 Lifusteine 立氟司坦 Mucokinetics drugs(痰液调节药) Bromhexine 溴己新 Ambroxol 氨溴索 Expectorants Ammonium chloride 氯化铵 • 恶心性祛痰药的代表药 • This causes the production of excess respiratory tract fluid which presumably is easier to cough up. • Ammonium salts are an irritant to the gastric mucosa and may induce nausea and vomiting. Expectorants Guaifenesin 愈创木酚甘油醚 • 刺激性祛痰药的代表药 • Effect and mechanism of action – increasing the volume and reducing the viscosity of secretions in the trachea and bronchi. – stimulates the flow of respiratory tract secretions, – allowing ciliary movement to carry the loosened secretions upward toward the pharynx – increase the efficiency of the cough reflex – facilitate removal of the secretions Mucolytic drugs Bromhexine 溴己新 • Bromhexine is a synthetic derivative of the herbal active ingredient vasicine(鸭嘴花碱) • used in the treatment of respiratory disorders associated with viscid or excessive mucus. Mucolytic drugs Pharmacological effect • Bromhexine supports the body's own natural mechanisms for clearing mucus from the respiratory tract. • Secretolytic effect : – increases the production of serous mucus in the respiratory tract – enhances mucus transport by reducing mucus viscosity • secretomotoric effect: – enhances mucus transport by activating the ciliated epithelium • antioxidant effect Mucolytic drugs N-Acetylcysteine N乙酰半胱氨酸,NAC • a derivative of cysteine; • Pharmacological effect: – Antioxidant and liver protecting effects-- a dietary supplement : – Breaks disulfide bonds in mucus and liquefies it, making it easier to cough up.-- cough therapy: – Prevention of radiocontrast-induced nephropathy -Nephroprotective agent Mucoregultor Carbocysteine 羧甲司坦 • Mucolytic • Carbocisteine is produced by alkylation of cysteine with chloroacetic acid. • Pharmacological effect – Reduces the viscosity of sputum allowing the sufferer to bring up sputum more easily. • Carbocisteine should not be used with antitussives (cough suppressants) or medicines that dry up bronchial secretions. Mucolytic drugs Erdosteine 厄多司坦 • it is a thiol derivative. Action • Mucolytic • free radical scavenging activity. • modulates mucus production and viscosity • increases mucociliary transport, • It also exhibits inhibitory activity against the effects of free radicals produced by cigarette smoke. Clinical use: • chronic obstructive lung disease : reduced cough (both frequency and severity) and sputum viscosity more quickly and more effectively than placebo and reduced the adhesivity of sputum more effectively than bromhexine 30 mg twice daily. • Co-administration of erdosteine and amoxicillin in patients with acute infective exacerbation of chronic bronchitis resulted in higher concentrations of the antibiotic in the sputum, leading to earlier and more pronounced amelioration of clinical symptoms compared with placebo. • a low incidence of adverse events, most of which are gastrointestinal and generally mild. Mucokinetic drugs Ambroxol ( 氨溴索,沐舒坦) • 全肺动力型排痰剂 • a mucoactive drug with several properties including • – secretolytic and secretomotoric actions that restore the physiological clearance mechanisms of the respiratory tract – It stimulates synthesis and release of surfactant by type II pneumocytes. – It promotes mucus clearance, facilitates expectoration and eases productive cough local anaesthetic effect – a very potent inhibitor of the neuronal Na+ channels • anti-inflammatory properties Clinical use: • upper respiratory tract infections and other lung problems, including chronic inflammatory pulmonary conditions; Mucokinetic drugs Ambroxol Side Effects Gastrointestinal Side Effects • including diarrhea, heartburn, indigestion, and occasionally nausea and vomiting. Allergic Reactions • rarely, mainly involve skin rashes, hives and dermatitis, as well as possible swelling. Intravenous Side Effects • Intravenous ambroxol has been associated with chills, intense headaches, shortness of breath and weakness. Mucoactive drugs Fudosteine (福多司坦) • a cysteine derivative • Inhibit MUC5AC mucin hypersecretion by reducing MUC5AC gene expression • Iihibition of extracellular signal-relatedI kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in vivo and extracellular signal-related kinase in vitro. Mucoactive drugs Myrtol (稀化黏素,桃金娘油) • an essential oil derived from the Myrtle plant (Myrtus communis) • consisting mainly of three monoterpenes: – (+)α-pinene(蒎烯 ) – d-limonene (柠檬烯 ) – 1,8-cineole (桉叶素 ) Pharmacological effects: • Increases mucociliar clearance • Mucosecretolytic effects. • Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties Clinical use: – acute and chronic bronchitis and sinusitis 祛痰药作用比较表 药物 作用机制 用法 临床应用 氯化铵 增加分泌物 口服 急、慢性呼吸道 炎症痰多不易咳 出者 溴己新 裂解粘多糖 口服 痰液粘稠难于咳 出 雾化吸入 粘痰阻塞气道 乙 酰 半 胱 氨 裂解粘蛋白 酸 气管滴入 Bronchodilators (支气管扩张药) Drugs acting on respiratory system Cough antitussive drugs centrally acting peripherally acting Sputum expectorant drugs sputum-diluting drugs mucolytic drugs Asthma antiasthmatic drugs Bronchodilators receptor agonists theophyllines muscarinic antagonists Anti-inflammatory drugs glucocorticosteroids mediator release inhibitors Antiasthmatic drugs Immunological and non-immunological stimuli Airway inflammation bronchoconstriction glucocorticosteroids 2 receptor agonists Disodium cromoglycate Muscerinic antagonists Leukotriene modifiers Theophylline Airway hyperresponsiveness Wheezing (asthmatic symptoms) Bronchodilators Receptor agonists Non-selective:adrenaline, isoprenaline 2-selective: salbutamol, terbutaline, salmeterol, formoterol Theophyllines: aminophylline Muscarinic antagonists: ipratropium bromide receptor agonists non-selectivity 去甲肾上腺素 肾上腺素 异丙肾上腺素 沙丁胺醇 福莫特罗 2 receptor selective agonists β2-AR agonists • Short-acting β2-adrenergic receptor agonists(SABAs) • 1. Albuterol (Salbuterol 沙丁胺醇 ) • 2. Fenoterol(菲诺特罗,酚间羟异丙肾上腺素) • 3. Terbutaline (特布他林) • Long-acting β2-adrenergic receptor (LABAs) • 1. Formoterol (福莫特罗) • 2. Salmeterol (沙美特罗) Ultra-long-acting β2-adrenergic receptor agonists (ultra-LABA) • 1. Indacaterol (茚达特罗) • 2. Olodaterol (奥达特罗 ) • 3. Vilanterol (维兰特罗 ) • 4. Carmoterol (卡莫特罗) • 5. LAS100977 • 6. PF-610355 • 7. AZD3199. Short-acting β2-AR agonists (SABAs) Salbuterol 沙丁胺醇 1. Pharmacological effects Relaxing bronchial smooth muscles 2. Clinical uses Controlling asthmatic symptoms Given by inhalation, oral or injection Dysfunction of metabolism (ketoacidosis,raises blood sugar levels, elevated blood levels of fatty acids and glyceroletc.) mild appetite suppression, headache, nausea, and sleep disturbances Side effect • Increased heart rate and palpitations • they should be used with caution in patients with hyperthyroidism or cardiovascular disease (arrhythmias, hypertension, QT-interval prolongation) • transient decrease in partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) despite concomitant bronchodilation. • used with caution in patients with diabetes because of the risk of ketoacidosis. • 2-AR stimulation in the liver induces glycogenolysis and therefore raises blood sugar levels Selectivity of 2 agonists Bronchial dilators 2 receptor selective agonists: Long-acting 2 receptor agonists (LABA) Formoterol Salmeterol 福莫特罗 沙美特罗 Bronchial dilators Theophyllines Aminophylline -- -- O H3C N O -- . NH N CH3 氨茶碱 CH2NH2 . 2H2O CH2NH2 N -- 2 Theophyllines: One type of xanthine derivatives (甲基黄嘌呤类衍生物) Theophyllines history Bronchial dilators 1. Pharmacological effects Inhibiting phosphodiesterase(PDE); Blocking adenosine receptors; Increasing catecholamine release; Immunomodulation; Increasing contractility of respiratory muscle(diaphragm muscle); Diuretic, CNS stimulation, Gastric acid secretion, etc. Bronchial dilators 2. Clinical uses Bronchial asthma (p.o., i.v.) Others: acute pulmonary edema, etc. Slow-release theophylline (for control of nocturnal asthma) is the most commonly used methylxanthine. Aminophylline pentoxifylline, is promoted as a remedy for intermittent claudication; Common adverse effects: Gastrointestinal distress, tremor, and insomnia. Severe nausea and vomiting, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, Seizures Very large overdoses (eg, in suicide attempts) are potentially lethal because of arrhythmias and seizures. Beta blockers are useful in reversing severe cardiovascular toxicity from theophylline. Muscarinic antagonists Presynaptic mediator involved in ACh release (neurojunctional plaque). Muscarinic antagonists Short-acting muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) antagonists(SAMAs) 1. Atropine methonitrate 2. Ipratropium bromide (异丙托溴铵) 3. Oxitropium bromide (氧托溴铵) Long-acting long mAChR antagonists (LAMAs) Tiotropium bromide (噻托溴铵) Novel long-acting mAChR antagonists 1.Glycopyrronium bromide (格隆溴铵) 2. Aclidinium bromide (阿地溴铵) 3. Other muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists under development. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) antagonists ipratropium bromide (异丙托溴铵); oxitropium bromide (氧托溴铵); tiotropium bromide (噻托溴铵). 气道松弛作用强度: 异丙托溴铵<氧托溴铵<噻托溴铵; 作用持续时间: 异丙托溴铵<氧托溴铵<噻托溴铵. Mechanism of Action and Effects • When given by aerosol, ipratropium and tiotropium competitively block muscarinic receptors in the airways and effectively prevent bronchoconstriction mediated by vagal discharge. • Muscarinic antagonists reverse bronchoconstriction in some asthma patients (especially children) and in many patients with COPD. • They have no effect on the chronic inflammatory aspects of asthma. Long-acting Muscarinic antagonists(LAMA) Clinical Use and Toxicity • Ipratropium and tiotropium are useful in one third to two thirds of asthmatic patients; β2 agonists are effective in almost all. • For acute bronchospasm, therefore, the β agonists are usually preferred. • However, in COPD, which is often associated with acute episodes of bronchospasm, the antimuscarinic agents may be more effective and less toxic than β agonists. Mechanisms of bronchodilatory action of antimuscarinic agents and beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists. Antimuscarinics block the binding of acetilcholine (ACh) to M3 muscarinic receptor, thereby inhibiting smooth muscle cell contraction. Beta2adrenergic receptor agonists bind to beta2-adrenergic receptor and induce a cascade of signal transduction events that ultimately lead to smooth muscle relaxation. Novel class of Brochodilators Aerosol inhalation 定量手控 气雾器 Spacer used for aerosol inhalation Spacer will aid patients to inhale the aerosolized drugs easier Outcome of different sized particles: > 10μm: mouth and oropharynx < 0.5μm: inhaled to the alveoli and subsequently exhaled without being deposited in the lung 1-5μm: the most effective Drugs for treatment of respiratory diseases Huifang Tang Department of pharmacology Zhejiang University, school of medicine [email protected] Antiasthmatic drugs Immunological and non-immunological stimuli Airway inflammation bronchoconstriction glucocorticosteroids 2 receptor agonists disodium cromoglycate theophylline leukotriene modifiers muscerinic antagonists Airway hyperresponsiveness Wheezing (asthmatic symptoms) Antiasthmatic drugs Airway pathological changes in pathogenesis of bronchial asthma Anti-inflammatory drugs • 抗炎平喘药 • Glucocorticosteroids: Inhaled steroids: beclomethasone(倍氯米松), budesonide(布地奈德), fluticasone(氟替卡松) Systemic steroids: hydrocortisone(氢化可的松), prednisone(强的松), dexamethasone(地塞米松) • PDE4 inhibitors: Roflumilast (罗氟司特) • Leukotriene (LT) modifiers: • • LT receptor antagonists: montelukast (孟鲁司特), zafirlukast (扎鲁司 特) 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors: zileuton (齐留通) • 抗过敏平喘药 • Inhibitors of mediator release: cromolyn sodium(色甘酸钠), nedocromil (奈多罗米) • H1 receptor antagonists: ketotifen (酮替芬) Antiasthmatic drugs Glucocorticosteroids Systemic corticosteroids hydrocortisone 氢化可的松 prednisone 泼尼松 dexamethasone 地塞米松 Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) beclomethasone dipropionate 二丙酸倍氯米松 budesonide 布地奈德 fluticasone propionate 丙酸氟替卡松 flunisolide 氟尼缩松 A. Glucocorticoid drugs 1. Pharmacological effects Mechanisms of glucocorticoid actions (1) Effects on metabolisms (2) Permissive action (3) Anti-inflammatory effects (4) Effects on immune and allergy (5) Anti-shock (6) Other effects antipyretic effects effects on blood and blood-forming organs skeletal system CNS effects A. Glucocorticoid drugs Anti-inflammatory effects Acute: inhibiting microvascular leakage leukocyte infiltration Chronic: inhibiting fibroblast proliferation deposition of collagen cicatrization (瘢痕形成) • Mechanism of anti-inflammatory action of corticosteroids in asthma. Action mode of glucocorticoid drugs CBG: corticosteroid binding globulin S: glucocorticoid steroids GR: glucocorticoid receptor HSP: heat shock protein IP: immunophilin GRE: glucocorticoidresponse element Effect of glucocorticoids on transcription of genes relevant to asthma Increased transcription (trans-activation) • Lipocortin-1 • β2-Adrenoceptors • Secretory leukocyte inhibitory protein • IkB-a (inhibitor of NF-kB) • MKP1 (inhibits MAP kinase pathways) • Glucocorticoid inducible leucine zipper (GILZ) • Anti-inflammatory or inhibitory cytokines IL-10, IL-12, IL-1 receptor antagonist Decreased transcription (trans-repression) • Inflammatory cytokines: IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-13, IL-15, TNF-a, GM-CSF, SCF, TSLP • Chemokines: CCL1, CCL5, CCL11, CXCL8 • Inflammatory enzymes: Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), inducible cyclo-oxygenase (COX-2) Inducible phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) • Inflammatory peptides: Endothelin-1 • Mediator Receptors: Neurokinin (NK1)-, bradykinin (B2)-receptors • Adhesion molecules: ICAM-1,VCAM-1 Non-genomic mechanisms of action of glucocorticoids. C. Boardman et al. / Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 29 (2014) 129e143 • Effect of corticosteroids on inflammatory and structural cells in the airways. A. Glucocorticoid drugs 2. ADME and properties of commonly used drugs Cortisone and prednisone are reduced and transformed to hydrocortisone and prednisolone (active forms) in the liver Metabolism will be increased by hepatic enzyme inductors (phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampine, etc.) 理想的 ICS需具备药代动力学的特性 • 合适的粒径 • 适宜的油/水分布比值 – 高受体亲和力:脂溶性 – 高气道滞留率:水溶性、酯化作用、脂溶性 • 适宜的表观分布容积 • 适宜的半衰期 • 肝脏首过效应强,生物利用度低 2017/5/23 Antiasthmatic drugs Chemical structure of 4 kinds inhalation glucocorticosteroids 二丙酸倍氯米松 (BDP) HO CH2OCOC2H5 C=O OCOC2H5 CH3 布地奈德 (BUD) CH2OH C=O HO O H C C3H7 O Cl O O H 丙酸氟替卡松 (FP) HO H SCH2F 糠酸莫米他松 Cl (MF) C=O OCOC2H5 CH3 HO Cl F O O F O C=O O CCH3 Receptor-binding affinity of inhaled corticosteroids to the glucocorticoid receptor 布地奈德 布地奈德是新一代糖皮质激素,具有呼吸道选择性 16 α和17α位加入了亲脂基团 - 增加了糖皮质激素受体的亲和力 - 增加了摄取及局部的应用 - 全身吸收后快速代谢失活 布地奈德肺内酯化作用 O = -C-(CH2)nCH3 布地奈德酯化作用 − 延长了抗炎作用时间 − 增加了呼吸道的选择性 Atp,adenosine triphosphate;CoA,coenzyme A. Tunek A et al.Drug Metob Dispos 1997;25:1311-1317;Miller-Larsson A et al.Drug Metab Dispos 1998;26:623-630. ICS药理学和药代动力学参数对全身效应的影响 布地奈德 氟替卡松 倍氯米松 糖皮质激素效应 高 高 中等/低 脂溶性 中等/高 高 低 分布容积(L) 183 318 20 气道滞留率 最高 高 低 经口吸收药物的首 过清除 高 较高 低 半衰期 2.8h 14.4h 0.1h 全身效应 低 中等 高 A. Glucocorticoid drugs 3. Clinical uses ICS are now recommended as first-line therapy for all patients with persistent asthma, including children. Current guidelines suggest that high doses of ICS should be used only in patients with severe disease (FEV1 < 50% predicted) who have frequent exacerbations (≤2 per year) which would comprise about 10% of patients, whereas currently high-dose ICS are used in approximately 80% of patients with a clinical diagnosis of COPD. Interaction with β2-adrenergic receptors Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology, 2006:231 Interactions and effects on gene expression that may occur between long-acting b2-adrenoceptor agonists, or other cAMP-elevating agents, and glucocorticoids 4.Adverse effects Adverse effects of glucocorticoid drugs: Effects resulting from continued used of large doses B. PDE4 inhibitors Roflumilast (罗氟司特) 1. Pharmacological effects Inhibits inflammation Bronchial dilating effect Attenuates bronchial remodeling 2. Clinical uses Approved for the treatment of asthma and COPD (2010), once daily 3. Adverse effects Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, weight loss, headache, insomnia, depression, etc. B. PDE4 inhibitors Klaus F. Rabe, BJP,2011 B. PDE4 inhibitors • Combination of PDE4 inhibitor with ICS: – Enhanced the glucocorticoid function, suggesting its use as a glucocorticoid –sensitising • Combination of PDE4 inhibitor with LABAs(long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonist): – Enhance anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid activity above the level produced by an inhaled glucocorticoid/LABA combination therapy alone. because LABAs and PDE4 inhibitors act on the same signaling pathway (i.e. they increase cAMP synthesis and block cAMP degradation, respectively), they may act synergistically. F1000Prime Rep. 2015 Feb 3;7:16. C. Leukotriene modifiers (LTM) • CysLT1 receptor antagonist – montelukast (孟鲁司特) – zafirlukast (扎鲁司特) • 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors – zileuton (齐留通) Effects of cysteinyl-leukotrienes on the airways and their inhibition by anti-leukotrienes. AS, aspirin sensitive; 5-LO, 5-lipoxygenase; LT, leukotriene; PAF, platelet-activating factor. C. Leukotriene modifiers (LTM) Zafirlukast (Accolate, 扎鲁司特) • an oral LTRA • Reducing constriction of the airways and buildup of mucus in the lungs and inflammation of the breathing passages. • Clinical use: twice daily • maintenance treatment of asthma, often used in conjunction with an inhaled steroid and/or longacting bronchodilator. C. Leukotriene modifiers (LTM) Montelukast (Singulair and Montelo-10, 孟鲁司特) • it blocks the action of leukotriene D4 (and secondary ligands LTC4 and LTE4) on the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor CysLT1 in the lungs and bronchial tubes by binding to it. • reduces the bronchoconstriction • Clinical use: once daily – Asthma:maintenance treatment of asthma and to relieve symptoms of seasonal allergies – exercise induced bronchospasm – allergic rhinitis – urticaria • it is not useful for the treatment of acute asthma attacks. C. Leukotriene modifiers (LTM) Adverse effects • generic adverse reactions: – – – – – gastrointestinal disturbances Headaches hypersensitivity reactions sleep disorders increased bleeding tendency • Churg–Strauss syndrome • Drowsiness C. Leukotriene modifiers Zileuton (Zyflo, 齐留通) • an orally active inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase – Inhibits leukotrienes (LTB4, LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) formation. • Clinical use: taken four times per day – Zileuton is used for the maintenance treatment of asthma. • Adverse effects – sinusitis(鼻窦炎), nausea , pharyngolaryngeal pain (咽喉疼痛) D. Inhibitors of mediator release Disodium cromoglycate 色甘酸二钠 ( cromolyn ) (色甘酸钠) Sodium nedocromil (萘多罗米钠) D. Inhibitors of mediator release 1. Pharmacological effects Inhibiting mediator release from mast or other cells Inhibiting sensory neuropeptide release 2. Clinical uses Prevention of allergic asthma Acting slowly (2-4 weeks) 3. Adverse effects Oropharyngeal irritation Cromolyn Inhibits mediator release from mast cells D. Inhibitors of mediator release Other inhibitors of mediator release: Sodium nedocromil(萘多罗米钠) Inhibiting mediators release from mast cell or other cells, the effect is better than disodium cromoglycate. Ketotifen(酮替芬) Inhibiting mediators release, and antagonizing H1 receptor. GINA stepwise approach for managing asthma in patients ≥ 5 years of age with persistent mild or moderate disease, focus on step 3 World Allergy Organ J. 2010 Feb; 3(2): 16–22. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. (2014) 15(1):85-96 Reference Pharmacology and therapeutics of bronchodilators. Cazzola M, Page CP, Calzetta L, Matera MG. Pharmacol Rev. 2012 Jul;64(3):450-504. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004580. Review.