* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download VACM-1! - Hope College
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
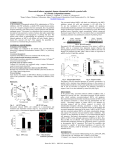
VACM-1! By Michael Hledin and Gabe Marquez Introduction VACM-1 stands for Vasopressin-Activated Calcium Mobilizing Receptor AKA Cullin5 • It encodes a protein called 93 kDa, and inhibits (stops) cellular growth. • VACM-1 is naturally expressed in blood vessel cells and is associated with complexes that destroy proteins in the cell. Uses on cancer • VACM-1 stops cell growth, therefore, if used on cancer cells, it should stop the growth of cancerous tumors on cells. Hypothesis • If we increase VACM1 in vascular cells it will decrease cell growth which will help prevent cancer cell growth. • If we increase VACM1 in cancerous cells, it will decrease also cell growth. What We Do • We mutate VACM-1 in cells and look at changes in cell growth. • Our method is to find a drug to induce growth of VACM-1 in cells. Method 1 • Our first method is for RAMEC cells, which are found in rats. We take a plate of cells as shown below, and scratch a cross into each well. We then treat the cells with different doses of a drug, called PMA which induces cell growth. After the cells are treated, we monitor their growth for a few days. If the scratch has increased or gotten wider, then the drugs have stopped or slowed cell growth, but if it has gotten smaller, the drugs have increased cell growth. Method 2 • Our second method is for T47D cells which are the primary cancer cells. Since these grow slower then RAMEC cells, it would take too long to scratch them. Therefore, we simply count the number of cells we have before and after we treat them. In these cells, we use a drug called resveratrol which is found in wine. Below we have graphs that show the effect that different doses of resveratrol had on T47D cells. 40 ug/ml Resveratrol 5 ug/ml Resveratrol 90.00% Change in Growth 100.00% 80.00% 60.00% CMV Control Cells 40.00% VACM-1 Transfected cells 20.00% Change in Growth 120.00% 40.00% -10.00% CMV control cells 0 1 VACM-1 Transfected cells -60.00% 0.00% -20.00% 0 1 3 -110.00% Time (days) -40.00% Time(days) 3 Conclusions • When cells that had VACM1 were treated with drugs, growth was decreased much more then in cells with no VACM1. This makes VACM1 an important regulator of cell growth and a target for cancer drugs. Acknowledgements • • • • • • The REACH Program Professor Hledin The Hledin lab especially Justin Lubbers Mrs. Harper Biology and Chemistry departments Hope College