* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06_10_13.html
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aza-Cope rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Vinylcyclopropane rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
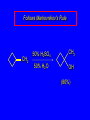
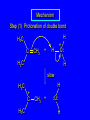
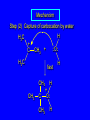
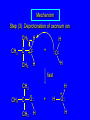
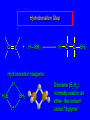
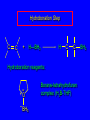
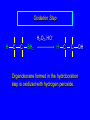
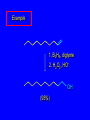
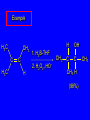
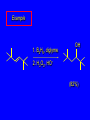
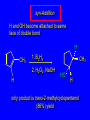
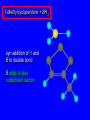
6.10 Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes C C + H—OH H C C OH reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% H2SO4-50% H2O Follows Markovnikov's Rule H3C C H3C CH3 H 50% H2SO4 C CH3 50% H2O CH3 C CH2CH3 OH (90%) Follows Markovnikov's Rule CH2 50% H2SO4 CH3 50% H2O OH (80%) Mechanism involves a carbocation intermediate is the reverse of acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols to alkenes H3C H+ C H3C CH3 CH2 + H2O CH3 C OH CH3 Mechanism Step (1) Protonation of double bond H H3C C CH2 + + O: H H3C H slow H3C H3C H + C CH3 + :O: H Mechanism Step (2) Capture of carbocation by water H3C H + C :O: CH3 + H3C fast CH3 CH3 C CH3 H + O: H H Mechanism Step (3) Deprotonation of oxonium ion CH3 CH3 C H : +O CH3 H + :O: H H fast H CH3 CH3 C CH3 .. O: H + H + O: H Relative Rates Acid-catalyzed hydration ethylene CH2=CH2 1.0 propene CH3CH=CH2 1.6 x 106 2-methylpropene (CH3)2C=CH2 2.5 x 1011 The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed, and the faster the reaction rate. Principle of Microscopic Reversibility H3C H+ C H3C CH3 CH2 + H2O CH3 C CH3 OH In an equilibrium process, the same intermediates and transition states are encountered in the forward direction and the reverse, but in the opposite order. 6.11 Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes Synthesis Suppose you wanted to prepare 1-decanol from 1-decene? OH Synthesis Suppose you wanted to prepare 1-decanol from 1-decene? Needed: a method for hydration of alkenes with a regioselectivity opposite to Markovnikov's rule. OH Synthesis Two-step reaction sequence called hydroborationoxidation converts alkenes to alcohols with a regiochemistry opposite to Markovnikov's rule. 1. hydroboration 2. oxidation OH Hydroboration Step C C + H—BH2 H C C BH2 Hydroboration can be viewed as the addition of borane (BH3) to the double bond. But BH3 is not the reagent actually used. Hydroboration Step C C + H—BH2 H C C BH2 Hydroboration reagents: H H2B BH2 H Diborane (B2H6) normally used in an ether- like solvent called "diglyme" Hydroboration Step C + C H H—BH2 C C Hydroboration reagents: •• +O – BH3 Borane-tetrahydrofuran complex (H3B-THF) BH2 Oxidation Step H2O2, HO– H C C BH2 H C C OH Organoborane formed in the hydroboration step is oxidized with hydrogen peroxide. Example 1. B2H6, diglyme 2. H2O2, HO– OH (93%) Example H3C CH3 C H3C C H 1. H3B-THF 2. H2O2, HO– CH3 H OH C C CH3 H (98%) CH3 Features of Hydroboration-Oxidation hydration of alkenes regioselectivity opposite to Markovnikov's rule no rearrangement stereospecific syn addition Example 1. B2H6, diglyme OH 2. H2O2, HO– (82%) 6.12 Stereochemistry of Hydroboration-Oxidation Features of Hydroboration-Oxidation hydration of alkenes regioselectivity opposite to Markovnikov's rule no rearrangement stereospecific syn addition syn-Addition H and OH become attached to same face of double bond H CH3 1. B2H6 2. H2O2, NaOH H CH3 HO H only product is trans-2-methylcyclopentanol (86%) yield 6.13 Mechanism of Hydroboration-Oxidation 1-Methylcyclopentene + BH3 syn addition of H and B to double bond B adds to less substituted carbon Organoborane intermediate Add hydrogen peroxide OH replaces B on same side trans-2-Methylcyclopentanol