Document
... Aldehydes and Ketones—Nucleophilic Addition The Wittig Reaction • Since phosphorus is a second-row element, it can be surrounded by more than eight electrons. • Thus, a second resonance structure can be drawn that places a double bond between carbon and phosphorus. • Regardless of which resonance s ...
... Aldehydes and Ketones—Nucleophilic Addition The Wittig Reaction • Since phosphorus is a second-row element, it can be surrounded by more than eight electrons. • Thus, a second resonance structure can be drawn that places a double bond between carbon and phosphorus. • Regardless of which resonance s ...
amine
... Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones • Amines can be synthesized in a single step from aldehydes or ketones with ammonia in the presence of a reducing agent ...
... Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones • Amines can be synthesized in a single step from aldehydes or ketones with ammonia in the presence of a reducing agent ...
06_10_13.html
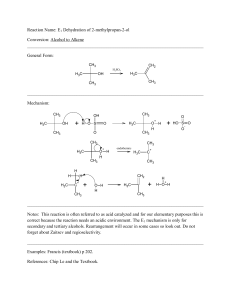
... The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed, and the faster the reaction rate. ...
... The more stable the carbocation, the faster it is formed, and the faster the reaction rate. ...
Enol esters: Versatile substrates in synthesis of fine and specialty
... acidic conditions with mostly retention of configuration. Both α-acyloxy ketones and their αhydroxy ketone derivatives, are essential in synthesis of alkaloids, sugars, antibiotics, terpenes and pheromones, for they function as stereodirective groups or chiral synthons. Zhu et al. practised the rear ...
... acidic conditions with mostly retention of configuration. Both α-acyloxy ketones and their αhydroxy ketone derivatives, are essential in synthesis of alkaloids, sugars, antibiotics, terpenes and pheromones, for they function as stereodirective groups or chiral synthons. Zhu et al. practised the rear ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... Acidity of Amines • NH3, RNH2, and R2NH are amphoteric: they may act as bases and acids • They are very weakly acidic – Will give up H+ to a very strong base • The conjugate base of an amine is called an amide (do not confuse with amide derivatives of carboxylic acids) ...
... Acidity of Amines • NH3, RNH2, and R2NH are amphoteric: they may act as bases and acids • They are very weakly acidic – Will give up H+ to a very strong base • The conjugate base of an amine is called an amide (do not confuse with amide derivatives of carboxylic acids) ...
PowerPoint ******
... “Wagner-Meerwein Rearrangements” must form the final products that are thermodynamically more stable than the starting materials. Some processes proceeding do appear to require uphill steps (formation of less stable carbocation). ...
... “Wagner-Meerwein Rearrangements” must form the final products that are thermodynamically more stable than the starting materials. Some processes proceeding do appear to require uphill steps (formation of less stable carbocation). ...
dr.ebtehal Lec3
... • Drug metabolism can occur in every tissue (e.g. gut, lung and kidney). However, the major drug metabolizing enzymes (DMEs) are expressed at the highest levels in the liver, which thus serves as the major organ of metabolic clearance • Drug metabolism serves to control the exposure of a potentially ...
... • Drug metabolism can occur in every tissue (e.g. gut, lung and kidney). However, the major drug metabolizing enzymes (DMEs) are expressed at the highest levels in the liver, which thus serves as the major organ of metabolic clearance • Drug metabolism serves to control the exposure of a potentially ...
Document
... This increase in the basicity of an amine by alkylation is slightly enhanced by introduction of a second alkyl group. Further alkylation of a 2o amine does further increase basicity, but only if measured in the gas phase. In the usual aqueous media, aminium ions from 1o and 2o amines are very effect ...
... This increase in the basicity of an amine by alkylation is slightly enhanced by introduction of a second alkyl group. Further alkylation of a 2o amine does further increase basicity, but only if measured in the gas phase. In the usual aqueous media, aminium ions from 1o and 2o amines are very effect ...
Amines
... when four things are bonded to a nitrogen atom, the nitrogen bears a positive charge name the compound as a salt replace the ending -amine (or aniline or pyridine or the like) by -ammonium (or anilinium or pyridinium or the like) and add the name of the anion ...
... when four things are bonded to a nitrogen atom, the nitrogen bears a positive charge name the compound as a salt replace the ending -amine (or aniline or pyridine or the like) by -ammonium (or anilinium or pyridinium or the like) and add the name of the anion ...
lec-3- 211( Elim+ Re..
... • Drug metabolism can occur in every tissue (e.g. gut, lung and kidney). However, the major drug metabolizing enzymes (DMEs) are expressed at the highest levels in the liver, which thus serves as the major organ of metabolic clearance • Drug metabolism serves to control the exposure of a potentially ...
... • Drug metabolism can occur in every tissue (e.g. gut, lung and kidney). However, the major drug metabolizing enzymes (DMEs) are expressed at the highest levels in the liver, which thus serves as the major organ of metabolic clearance • Drug metabolism serves to control the exposure of a potentially ...
Synthetic applications of ortho esters
... demonstrate a high level of stability toward strong nucleophiles and bases, most current applications are limited to protective group chemistry [2]. Compared to a carboxylic acid, the ortho ester removes the acidic hydroxyl group as well as the electrophilic carbonyl function and reduces the acidity ...
... demonstrate a high level of stability toward strong nucleophiles and bases, most current applications are limited to protective group chemistry [2]. Compared to a carboxylic acid, the ortho ester removes the acidic hydroxyl group as well as the electrophilic carbonyl function and reduces the acidity ...
Slide 1
... Since many iminium salts are unstable they are generally not isolate. As a result the reducing agent is added to the reaction mixture so that the iminium salt can be reduced as it is formed. Only very weak reducing agents can be used in this reaction to avoid reduction of the starting aldehyde or ke ...
... Since many iminium salts are unstable they are generally not isolate. As a result the reducing agent is added to the reaction mixture so that the iminium salt can be reduced as it is formed. Only very weak reducing agents can be used in this reaction to avoid reduction of the starting aldehyde or ke ...
Full Text - Journal of the Indian Institute of Science
... and selective dehydrating agent, and can be successfully utilized for the preparation of alkenes from alcohols. However, it went into oblivion for nearly a decade soon after its discovery by E. M. Burgess in 1968. It was Peter Wipf who brought it to the attention of organic chemists through its exte ...
... and selective dehydrating agent, and can be successfully utilized for the preparation of alkenes from alcohols. However, it went into oblivion for nearly a decade soon after its discovery by E. M. Burgess in 1968. It was Peter Wipf who brought it to the attention of organic chemists through its exte ...
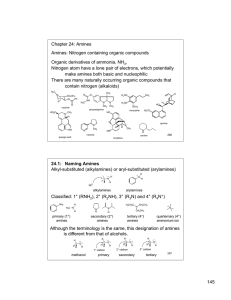
145 Chapter 24: Amines Amines: Nitrogen containing organic
... Table 24.1 (p. 899): pKa values of ammonium ions Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitr ...
... Table 24.1 (p. 899): pKa values of ammonium ions Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitr ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
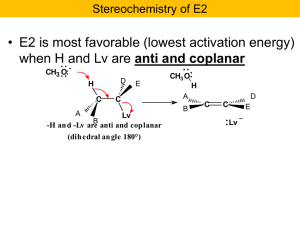
... Task: convert to a staggered structure wherein H and Br are anti and predict product. We will convert to a Newman and see what we get… Ph ...
... Task: convert to a staggered structure wherein H and Br are anti and predict product. We will convert to a Newman and see what we get… Ph ...
Amines
... intermediacy of an acyl azide l The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride with sodium azide l Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2 , a very stable leaving group l In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
... intermediacy of an acyl azide l The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride with sodium azide l Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2 , a very stable leaving group l In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
Organic synthesis and methodology related to the malaria drug artemisinin
... described. Our attempts to access the artemisinin family of anti-malarials through the total synthesis of dihydro-epi-deoxyarteannuin B and dihydroartemisinic acid will be discussed fully. Key features of the syntheses will include alkylation of menthone derivatives using Noyori’s zincate enolate me ...
... described. Our attempts to access the artemisinin family of anti-malarials through the total synthesis of dihydro-epi-deoxyarteannuin B and dihydroartemisinic acid will be discussed fully. Key features of the syntheses will include alkylation of menthone derivatives using Noyori’s zincate enolate me ...
amine
... Basicity of Amines • Aliphatic amines have about the same base strength, and are slightly stronger bases than NH3. • Aromatic and heterocyclic aromatic. • amines are considerably weaker bases than aliphatic amines. • Note that while aliphatic amines are weak bases by comparison with inorganic bases ...
... Basicity of Amines • Aliphatic amines have about the same base strength, and are slightly stronger bases than NH3. • Aromatic and heterocyclic aromatic. • amines are considerably weaker bases than aliphatic amines. • Note that while aliphatic amines are weak bases by comparison with inorganic bases ...
amine cured-epoxy matrices
... Epoxy resins can be cured with a variety of compounds called curing agents which are also known as curatives, hardeners, or converters. Of the many classes/types of curing agents, amines are most widely utilized as curing agents in epoxy matrices for high performance composites. This produces a hete ...
... Epoxy resins can be cured with a variety of compounds called curing agents which are also known as curatives, hardeners, or converters. Of the many classes/types of curing agents, amines are most widely utilized as curing agents in epoxy matrices for high performance composites. This produces a hete ...
Chapter 1--Title - Chemistry Workshop
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
Chapter 1--Title
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
... The acyl azide is obtained from an acid chloride Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
Chapter 8
... ◦ When four atoms or groups of atoms are bonded to a nitrogen atom, as for example CH3NH3+, nitrogen bears a positive charge and is associated with an anion as a salt. ◦ Name the compound as a salt of the corresponding amine. ◦ Replace the ending –amine (or aniline or pyridine or the like) by -ammon ...
... ◦ When four atoms or groups of atoms are bonded to a nitrogen atom, as for example CH3NH3+, nitrogen bears a positive charge and is associated with an anion as a salt. ◦ Name the compound as a salt of the corresponding amine. ◦ Replace the ending –amine (or aniline or pyridine or the like) by -ammon ...
Chapter 20 Amines - FIU Faculty Websites
... Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...
... Rearrangement of the acyl azide occurs with loss of N2, a very stable leaving group In the last step, the isocyanate is hydrolyzed by adding water ...