* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - Ms. Racette`s Wiki
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
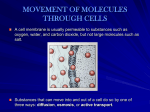
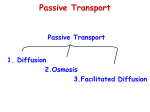
Cells Section 3-3: Cell Processes Metabolism The sum of all building-up and breaking-down activities that occur in a living cell Respiration The process in which simple food substances such as glucose are broken down and the energy they contain captured in high energy molecules that can be used as fuel by the cell Aerobic Respiration Requires oxygen Occurs in the mitochondria C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2+ 6H2O +energy (glucose) (ATP) Aerobic Respiration Although the equation is simple the process is complicated, involving many different molecules and many steps Anaerobic Respiration Does not use oxygen Provides much less energy Fermentation (such as the process used to make wine) is a form of anaerobic respiration Used by yeast that produce alcohol and carbon dioxide Photosynthesis Occurs in chloroplasts Also a very complex process 6CO2+ 6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 (glucose) The energy is captured from light by chlorophyll Diffusion The process by which molecules of a substance move from an area of higher concentration of that substance to areas of lower concentration of that substance Occurs because of the constant motion of molecules that causes them to spread out until they are evenly distributed in the available volume Diffusion Is a physical process that does not require the input of energy from a living organism A B C Diffusion into a Cell Diagram by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal, released to public domain Osmosis The diffusion of water into or out of a cell Many single-celled organisms that live in fresh water use contractile vacuoles to pump excess water out of the cell. The water enters the cell by osmosis. Semi-permeable Membranes Cell membranes are semi-permeable or selectively permeable This means that only certain molecules can diffuse through them including: Water Oxygen Carbon dioxide Small food molecules Osmosis Lower Concentration of Water Molecules Higher Concentration of Water Molecules Of Salt Of Salt Active Transport The process by which a cell moves molecules into and out of the cell that cannot diffuse through the membrane Requires energy to work Active Transport One method uses special transport molecules (proteins) that pick up a specific substance on one side of the membrane and moves it to the other side This is how ions of calcium (Ca), potassium (K) and sodium (Na) move Active Transport Diagram by Mariana Ruiz Villarreal, released to public domain Active Transport A second type of active transport is called phagocytosis. A cell surrounds a food particle with a pocket of cell membrane which pinches off into the cell to form a food vacuole Active Transport-Phagocytosis Drawing of an ameba engulfing a bacterium