* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extracellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle by Signal Transduction
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Tyrosine kinase wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
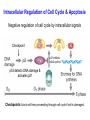
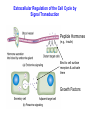
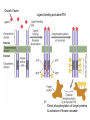
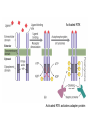
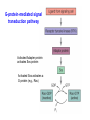
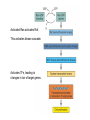
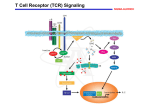
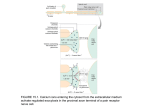
Intracellular Regulation of Cell Cycle & Apoptosis Negative regulation of cell cycle by intracellular signals Checkpoint p21 inhibits cdk2-cyclinA p53 detects DNA damage & activates p21 Checkpoints: block cell from proceeding through cell cycle if cell is damaged. Positive Regulation of Cell Cycle Kinase Cascade: Other signals induce phosphorylation of certain kinases. These kinases phosphorylate other kinases, activating them, etc. Eventually, phosphorylate certain TFs, activating them. Express genes needed to progress through cell cycle. Positive Regulation of Apoptosis Damaged mitochondria leak mitochondria proteins into cytoplasm. Ex: cytochrome c binds to Apaf (Apoptosis Pathway Activating Factor) Apaf-cytochrome c activates initiator caspase Negative Regulation of Apoptosis Bcl-2 inhibits activity of Apaf: Possibly involves: (a) Binding to Apaf (b) Prevent mitochondria from releasing cyto. c Extracellular Regulation of the Cell Cycle by Signal Transduction Peptide Hormones (e.g., Insulin) Bind to cell surface receptors & activate them Growth Factors Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) Transmembrane proteins Growth Factor (Ligand) binds to extracellular domain of receptor protein Plasma membrane Activates cytoplasmic domain (kinase) Growth Factor Ligand binding activates RTK Direct phosphorylation of target proteins & activation of kinase cascade Activated RTK Activated RTK activates adapter protein G-protein-mediated signal transduction pathway Activated Adapter protein activates Sos protein Activated Sos activates a G protein (e.g., Ras) G-proteins Active when bound to GTP Inactive when bound to GDP GTP GDP Activated Ras activates Raf. This activates kinase cascade. Activates TFs, leading to changes in txn of target genes. Classes of Growth Factors Mitogens stimulate cell division Ex: Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Activates signal transduction pathway that promotes cell division. Inhibitors of cell division Activate signal transduction pathways that inhibit cell division. Ex: TGFb inhibits phosphorylation of Rb