* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Membrane Transport notes
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
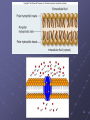
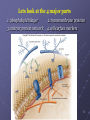
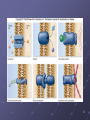
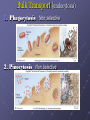
Cell Membrane Transport Membrane Structure Membrane is composed of... a. -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer b. -proteins inserted in bilayer for movement of molecules c. – carbohydrates for cell to cell recognition d. – cholesterols to keep membrane flexible We describe cell membranes as a fluid mosaic model fluid mosaic model animation 4 Lets look at the 4 major parts 1. phospholipid bilayer 3. interior protein network 2. transmembrane proteins 4. cell surface markers 5 Membrane structure is visible using an electron microscope. Transmission electron microscopes (TEM) can show the 2 layers of a membrane. 6 Membrane Proteins have many functions 1. transporters 2. enzymes 3. receptors 4. identity markers 5. cell-to-cell adhesion 6. attachments to cytoskeleton 7 8 Proteins move things by… I. Passive transport : 1. no energy is required 2. moves substances from high concentration to low concentration II. Active transport: 1. requires energy (ATP) 2. moves substances from low concentration to high concentration Bulk Transport Bulk transport is accomplished by 1. endocytosis – movement of substances into the cell 2. exocytosis – movement of materials out of the cell 13 Bulk Transport (endocytosis) 1. Phagocytosis Non selective 2. Pinocytosis Non selective 3. Receptor mediated Substrate specific Bulk Transport (exocytosis) vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with membrane and release their contents to the exterior of the cell 16 lets see it all together...... “fluid mosaic model”