* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Discovery of Cells
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
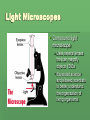
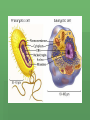
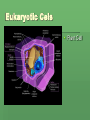
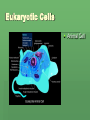
The Discovery of Cells Light Microscopes Anton van Leeuwenhoek The father of microscopy Used microscopes to study microorganisms Used a simple light microscope with one lens and a light Light Microscopes Compound light microscope Uses several lenses that can magnify objects 1500x Expanded science and allowed scientists to better understand the organization of living organisms. The Cell Theory Robert Hooke Observed dead cells of oak bark with a compound microscope Named box like structures CELLS Cells are the basic units of all living things Robert Hooke’s original image of bark. Matthias Schleiden German Scientist In 1830s concluded that all plants are composed of cells. Theodor Schwann Made similar observations on animals Concluded all animals are made up of cells Rudolf Virchow German Pathologist “Every cell comes from a cell.” Cell Theory 3 main ideas of the Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Singular cell organisms and Multicellular organisms. 2. The cell is the basic structure and organization of organisms. No matter how large an organism, it is made up of cells. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. A cell divides to form two identical cells. Electron Microscopes Vladimir Zworykin (seated) and James Hillier demonstrate an early electron microscope. Developed in the 1940s Uses a beam of electrons (not light) to magnify items as much as 500,000x allowing a view inside the cell. This occurs in a vacuum so that electrons do not collide with air particles 2 Types of Electron Microscopes pg 192 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Scans cells surface to provide scientist with its 3-D shape. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Allows scientist to study structures inside the cell. 2 Basic Cell Types 1. Prokaryotic – Do not have membrane-bound organelles. Most unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. Called prokaryotes. Organelles are specialized structures contained within a cell. 2. Eukaryotic -Cells containing membrane-bound organelles. Most multicellular organisms and are known as eukaryotes. Some unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. The Nucleus Robert Brown Scottish Scientist that observed eukaryotic cells and noted a prominent structure. Rudolf Virchow Concluded that this structure was responsible for cell division. This structure is what we now call a nucleus. Eukaryotic Cels Plant Cell Eukaryotic Cells Animal Cell