* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
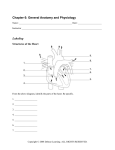
Chapter 3 CELLS CELL MEMBRANE • Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane • The cell membrane separates the cell from its external environment and neighboring cells • The cell membrane regulates the transport of molecules into and out of the cell © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. NUCLEUS • The nucleus is the most important organelle within the body • The nucleus contains DNA and protein arranged in a loose state called chromatin • Located within the nucleus are nucleoli which contain ribosomes and protein © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. CYTOPLASM • Cytoplasm is the semifluid material in which life functions take place • Organelles within the cytoplasm: – – – – – Centrosome Centrioles Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Golgi Apparatus - Lysosomes - Perioxisomes - Cytoskeleton - Pinocytic Vesicles © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. CELL DIVISION • Cells divide for two purposes: – Meiosis is the division of the sex cell or gamete – Mitosis is the division of the nucleus and the cytoplasm • Interphase • Anaphase • Metaphase • Telophase • Prophase © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • Cells produce proteins essential to life through protein synthesis • Within each cell the DNA determines the kinds of proteins that are produced © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. MOVEMENT OF MATERIALS ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES • Diffusion is the process whereby substances pass across a membrane generally from an area of greater concentration to one of lesser concentration • Osmosis is diffusion through a selective permeable membrane in which some materials can diffuse while others can’t © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. MOVEMENT OF MATERIALS ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES • Filtration - solutes move across a semipermeable membrane from high pressure to lower pressure • Active transport - molecules move across membrane from low to high concentration © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. MOVEMENT OF MATERIALS ACROSS CELL MEMBRANES • Phagocytosis is “cell eating” of substances within particles • Pinocytosis is “cell eating” of substances within solution © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. SPECIALIZATION • Specialized cells may lose the ability to perform some of the other life functions • Nerve and heart muscle cells cannot normally be replaced © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. DISORDERS OF CELL STRUCTURE • Tumors result when cell division is abnormal – Benign tumors are composed of cells confined to a local area – Malignant tumors continue to grow and crowd out healthy cells – Malignant tumors spread through the body by a process called metastasis © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc.