* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Steps of Meiosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
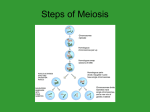
Meiosis The Production of Sex Cells How many chromosomes does a human body cell have? 46 How many chromosomes does a human sex cell have? 23 each The sex cell of females is called? • Egg The sex cell of males is called? • Sperm • Cell size: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begi n/cells/scale Why is it important that sex cells have half the usual number of chromosomes? • So that the fertilized egg receives a normal number of chromosomes During what process are sex cells made? • Meiosis – Produces sex cells with half the number of chromosomes. 7)How many steps? 1 (Not counting cytokinesis) 9 Prophase 2 8) How many chromosomes are in a human cell at the start of meiosis? • 46 9) How many times do the chromosomes make copies of themselves during meiosis? • once 1 Prophase 2 10) How many chromosomes are in the human cell after interphase? • 92 1 11) How many divisions does meiosis have? 2 Prophase 2 1 12) How many cells do you start with in meiosis? 1 How many cells do you end with? 4 Prophase 2 13) How many chromosomes are present in each human cell at the end of meiosis? 1 Prophase 2 23 14) Is each cell produced at the end of meiosis the same? Why? 1 Prophase 2 No To allow for genetic variations Steps of Meiosis 1. Interphase - each chromosome copies itself Steps of Meiosis 2. Prophase I - Homologous chromosomes (chromosomes that are the same) line up together Steps of Meiosis 3. Metaphase I - Homologous chromosomes line up in the middle and the spindle attaches to the centromere Steps of Meiosis 4. Anaphase I - The homologous chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell - The centromere does NOT split Steps of Meiosis 5. Telophase I - Cytokinesis occurs making 2 new cells - Each cell now has a copy of each homologous chromosome Steps of Meiosis • Between Telophase 1 and Prophase 2: The cell now rests, no duplication of chromosomes occurs Steps of Meiosis 6. Prophase II Steps of Meiosis 7) Metaphase II Steps of Meiosis 8. Anaphase II The centromere splits and sister chromatids separate Steps of Meiosis 9. Telophase II Result - 4 new daughter cells that are all genetically different - each new cell has half the number of chromosomes as the original cell Spermatogenesis • Males produce 4 sperm each round of meiosis Oogenesis • Females produce 1 egg (ovum) and 3 polar bodies each round of meiosis Fertilization • Fertilization will restore the original # of chromosomes • 23 from egg + 23 from sperm 46 total chromosomes to make a human