* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis - CashmereScience101
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
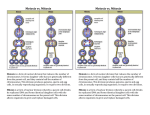
Starter 1. What is the purpose of Meiosis? 2. How many daughter cells are produced in Meiosis? 3. Are the daughter cells identical or different? 4. What causes the daughter cells to be different? Meiosis Meiosis is a special type of cell division used to produce sex cells (a.k.a. “gametes”) Only occurs in the sexual organs (e.g. testes of men or the ovaries of women) From one parent cell, four genetically different gametes are produced. Causes variation in the offspring because of crossing over and independent assortment 1. Chromosomes duplicate 92 chromosomes 2. Homologous chromosome pairs exchange pieces – called “cross over” 92 chromosomes Cross Over 3. Chromosomes line up in the middle 4. Chromosomes get pulled apart Independent Assortment 5. The cell splits into two daughter cells. 46 chromosomes + 46 chromosomes 6. Two genetically different daughter cells are produced. 46 chromosomes + 46 chromosomes 7. The chromosomes inside each daughter cell line up in the middle in a random way. 8. Chromosomes get pulled apart. 9. Each daughter cell splits into two. 10. Four daughter cells with only half the number of chromosomes are produced. Sequence of Events 1. Chromosomes duplicates 2. The chromosomes cross over. 3. Chromosomes line up in the middle 4. Chromosomes get randomly pulled apart and the parent cell splits into two daughter cells. 5. The chromosomes inside each daughter cell line up in the middle then get pulled apart. 6. Each daughter cell splits, producing a total of four daughter cells. Meiosis Meiosis is a special type of cell division used to produce sex cells (a.k.a. “gametes”) Only occurs in the sexual organs (e.g. testes of men or the ovaries of women) From one parent cell, four genetically different gametes are produced. Causes variation in the offspring because of crossing over and independent assortment