* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Transport active_transport1
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
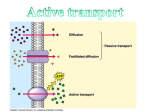
Q1 Does passive transport require energy? NO 1 Q2 What is the second type of transport? Active 2 Q3 What allows solutes to pass through a membrane? Proteins 3 What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? Diffusion is from a high concentration to low concentration and osmosis is the movement of water 4 5 Gummy Bear Osmosis They were each in a different solution, one with only water and one with salt water 6 Salt Water Gummy Bear in salt water: A cell’s cytoplasm is composed of a great amount of water. There is a greater percentage of water inside of cells than in the salt water surrounding the cells. This unequal amount of water inside and outside of the cell creates a concentration gradient. The cell wants to be in balance with its environment, so water will leave the cell. Water will leave rather than salt 7 Tap Water Gummy Bears in plain water: The cell is not only made up of water, there are also salts, sugars and proteins. Because there is only water in the beaker, there is a greater water concentration in the beaker than the cells of the gummy bear. This creates a concentration gradient, and to reach a balance, water enters the cells. As stated previously, water moves because it can freely pass through the cell membrane. The other molecules are too large. 8 Which one was hypotonic? Hypertonic? Why? 9 TOMORROW We are moving on to talking about Active Transport 10 Reminder about Cell Membranes: What is a cell membrane? Phospholipids Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail 11 Active Transport Requires energy from the cell Movement of particles from low concentration to high concentration Goes “uphill” Type 1: Pumps Particle binds to a transport protein Protein changes shape which requires energy Releases particle inside the cell Protein returns to original shape The SodiumPotassium Pump 13 Active Transport, cont. Movement of large particles, using membrane movement/reconfiguration Type 2: Endocytosis Movement of large particles INTO the cell Cell surrounds and takes in material from its environment Often used for nutrients or foreign invaders Type 3: Exocytosis Movement of large particles OUT of the cell Reverse process of endocytosis Used to expel wastes and secrete substances produced by the cell Endocytosis Exocytosis Endocytosis & Exocytosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4gLtk8 Yc1Zc 16 Basic types of transport 17 Membrane Transport Animation And once again, so you understand what she’s talking about… 18 Vocab Terms Passive Transport Active Transport Diffusion Equilibrium Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Endocytosis Exocytosis 19 Super Science Songs Cell Song Gotta Get That, ATP 20 Your assignment: Create a song using the information from this unit about cell organelles and cell transport You can use a song that you already know and alter the lyrics, or create a completely new song Complete lyrics will be due at the end of the period on Friday If you want to create a music video, you will receive extra credit, they will be due next Wednesday (12/19) 21 Requirements School appropriate lyrics Include at least 10 vocabulary words It needs to make sense when read/spoken At least three verses and a chorus that repeats 22