* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Theory - CGW-Life-Science
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
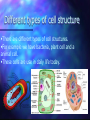
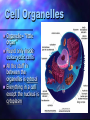
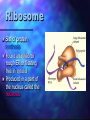
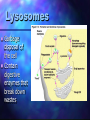
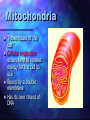
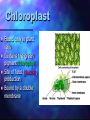
Cell Theory by: Khari Sanchez Some Cell Facts The average human being is composed of around 100 Trillion individual cells!!! It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter. There are millions of different types of cells. In the body, there are brain cells, skin cells, liver cells, stomach cells. Different types of cell structure There are different types of cell structures. For example we have bacteria, plant cell and a animal cell. These cells are use in daily life today. Plant and Animals Similarities They both have a have a nucleolus and nucleus. They both need a cell membrane. They both have to have to have a Centrosome. Both need to have rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Structure cell membrane nucleus nucleolus ribosomes ER Golgi centrioles cell wall mitochondria cholorplasts One big vacuole cytoskeleton Animal cells Yes Yes yes yes yes yes yes no yes no no yes Plant cells yes yes yes yes yes yes no yes yes yes yes Yes 3 Basic Components The 3 Basic Components of the Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. 3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. Cell Organelles Organelle= “little organ” Found only inside eukaryotic cells All the stuff in between the organelles is cytosol Everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Acts as skeleton and muscle Provides shape and structure Helps move organelles around the cell Made of three types of filaments Ribosome Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus Golgi Apparatus Looks like a stack of plates Stores, modifies and packages proteins Molecules transported to and from the Golgi by means of vesicles Lysosomes Garbage disposal of the cell Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes Mitochondria “Powerhouse of the cell” Cellular respiration occurs here to release energy for the cell to use Bound by a double membrane Has its own strand of DNA Chloroplast Found only in plant cells Contains the green pigment chlorophyll Site of food (glucose) production Bound by a double membrane Advantages of each kind of cell architecture Prokaryotes Eukaryotes simple and easy to grow can specialize fast reproduction multicellularity all the same can build large bodies Prokaryote cells are smaller and simpler Commonly known as bacteria 10-100 microns in size Single-celled (unicellular) or Filamentous (strings of single cells) Prokaryote cells are simply built (example: E. coli) cytoplasm: inner liquid filling DNA in one big loop pilli: for sticking to things flagella: for swimming ribosomes: for building proteins Eukaryotes are bigger and more complicated Have organelles Have chromosomes can be multicellular include animal and plant cells Eukaryote cells can be multicellular The whole cell can be specialized for one job cells can work together as tissues Tissues can work together as organs How Has The Cell Theory Been Used? The basic discovered truths about cells, listed in the Cell Theory, are the basis for things such as: Disease/Health/Medical Research and Cures(AIDS, Cancer, Vaccines, Cloning, Stem Cell Research. Some Parting Thoughts The cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. They are cells coming rub off and cells that are coming apart. That is the cycle of cell.