* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure & Function
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
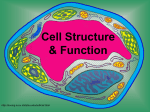
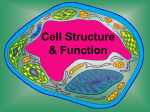
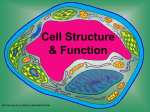
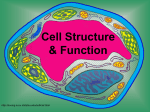
Cell Structure & Function http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html CELLS 5 Kingdoms each containing cells Use Prezi to identify the 5 Kingdoms Robert Hooke’s famous drawing of cork cells Cell Theory • The cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He examined very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that he remarked looked like the walled compartments of a honeycomb. • Hooke called them cells • However, Hooke did not know their real structure or function. [1] Cell Theory • The first man to witness a live cell under a microscope was Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, who in 1674 described the algae Spirogyra and named the moving organisms animalcules, meaning "little animals".[3]. • Leeuwenhoek probably also saw bacteria.[4] Spirogyra (Kingdom Protista) Bones are made of cells Muscles are made of cells Plant Cells Red Blood Cells Cells Nerve cells Nerve Cells White Blood Cell Red and White Blood Cells Cells are either multicellular (more than one) or unicellular (one) Animal and plant cells eukaryotes All plants are made of cells Plants Cells All animals are made of cells Comparison of Cells Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. Cells contain hereditary information (DNA) which is passed from cell to cell during cell division All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of structure in every living thing. All known living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are unicellular, i.e., made up of only one cell. Others are multicellular, composed of a number of cells. How many cells make up your body? • • • • • • • • • • My body is made of 1,000 cells My body is made of 10,000 cells My body is made of 100,000 cells My body is made of 1,000,000 cells My body is made of 10,000,000 cells My body is made of 100,000,000 cells My body is made of 1,000,000,000 cells My body is made of 10,000,000,000 cells My body is made of 100,000,000,000 cells My body is made of 1,000,000,000,000 cells What else is made of cells? Blue green Bacteria sometimes called Blue green Algae Algae Volvox (Kingdom Protista) Kelp forest (Algae) (Kingdom Protista) An Amoeba is unicellular (Kingdom Protista) Amoeba • Unicellular: “freeliving” can operate independently to survive • Example Volvox • Multicellular: works together with other cells as a larger part of the cell to survive • Example:Human Euglena are unicellular protist Yeast Cells: kingdom fungi (Fungi are made of cells) Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Cell Organelles and Parts • Organelle: membrane-bound structure within a cell that has a specific shape and function. • Examples: Nucleus, Mitochondria, Chloroplast Cell Theory • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Types of Cells • Cells can be subdivided into the following subcategories: • Prokaryotes: Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (though they do contain ribosomes). Bacteria are prokaryotes. • Eukaryotes: Eukaryotes have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, vacuoles,etc). Bacteria are made of cells called prokaryotes Bacteria-Eubacteria “Pro”: 1st Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes • Few internal structures • One-celled organisms, Bacteria http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html Eukaryotic • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes • Most living organisms Plant http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal “Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif Cell Parts Organelles Surrounding the Cell Cell Membrane/Plasma membrane • Outer membrane of cell that controls movement in and out of the cell • Double layer http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cell membrane Plasma membrane • Hydrophobic heads and hydrophilic tails • Phospholipid bilayer • Large proteins • cholesterol Cell Wall • Found in plant cells & bacteria • Supports & protects cells (UV rays and harsh conditions) http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Inside the Cell Nucleus • Directs cell activities • Separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane • Contains genetic material - DNA Nuclear Membrane • Surrounds nucleus • Made of two layers • Openings allow material to enter and leave nucleus http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chromosomes • Inside nucleus • Made of DNA • Contain instructions for traits & characteristics • 46 total in each cell** http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Nucleolus • Inside nucleus • Contains RNA to build proteins http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cytoplasm • A human cell system is approximately 75% water • The cytoplasm is the jelly-like watery fluid that makes up the cell. • Transports PROTEINS Cytoplasm • Gel-like mixture • Surrounded by cell membrane • Contains hereditary material Microfilaments and Microtubule • Helps to maintain shape of the cell. • Aid in cell division (mitosis and meiosis) Endoplasmic Reticulum • Moves materials around in cell • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes • Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Ribosomes • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins (PROTEINS SYNTHESIS) • Found on ribosomes & floating throughout the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Mitochondria • Produces energy ATP through chemical reactions – breaking down fats & carbohydrates • Controls level of water and other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Golgi Bodies • Protein 'packaging plant' • Move materials within the cell • Move materials out of the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Lysosome • Digestive 'plant' for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates (macromolecules) • Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal • Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution • Help plants maintain shape http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chloroplast • Usually found in plant cells • Contains green chlorophyll (pigment) • Where photosynthesis takes place http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html In Animal Cells only..Flagella • Long whip like extension used for movement In Animal Cells only..Centrioles • Short tubes necessary for cell division (reproduction) In Animal Cells only..Cilia • Short whiplike, hair like extension on the surface of some cells used for movement and gathering.