* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 1. What does it
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Barbara McClintock wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
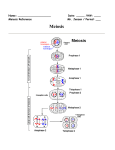
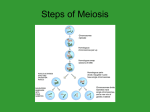
Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 1. What does it mean for two chromosomes to be, “homologous?” 2. How many homologous pairs of chromosomes do human beings have? 3. What is a, “tetrad?” 4. When are tetrads visible? 5. With regards to genetic diversity, what is the significance of tetrad formation? 6. In fruit flies, the gene for star eye and speck wing are on the same chromosome, yet offspring from star-eyed, speckwinged parents often inherit star eyes without the speck wings. How is this possible? Make a diagram to illustrate the process that is responsible for the recombination. Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 1. What does it mean for two chromosomes to be, “homologous?” If two chromosomes are homologous, they belong to the same pair. It is homologous chromosomes that line up together in metaphase of meiosis. Meiosis Mitosis Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 2. How many homologous pairs of chromosomes do human beings have? Human beings have 46 pairs of chromosomes 2n = 46 That means they must have 23 pairs of chromosomes 1n = 23 Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 3. What is a, “tetrad?” During late prophase and metaphase of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes line up in with their homologous pairs. Since each chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids, the pair of chromosomes consists of four chromatids, hence the name, “tetrad.” Tetrad Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 4. When are tetrads visible? During late prophase and metaphase of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes line up in with their homologous pairs. Since each chromosome is composed of two sister chromatids, the pair of chromosomes consists of four chromatids, hence the name, “tetrad.” Tetrad Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 5. With regards to genetic diversity, what is the significance of tetrad formation? Crossing over can occur only because chromosomes form tetrads during meiosis. Were it not for crossing over, traits on the same chromosomes would always be inherited together. Biology WarmUp: Meiosis Vocabulary Review 6. In fruit flies, the gene for star eye and speck wing are on the same chromosome, yet offspring from star-eyed, speckwinged parents often inherit star eyes without the speck wings. How is this possible? Make a diagram to illustrate the process that is responsible for the recombination. Though star eyes and speck wing are inherited together, they could be separated by crossing over, particularly if they were found far apart on the chromosome.