* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetic Variation
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
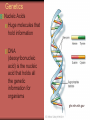
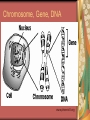
Genetic Variation www.alsa.org Goal To learn the basic genetic mechanisms that determines the traits expressed by individuals in a population Natural Selection Theory Variation in a population of organisms Results of Mutations Results of Immigration Result of survival features of individual organisms Natural Selection Theory Environments are dynamic Changing resources Climate (long term weather) Natural disasters Natural Selection Theory Selective Pressure Environmental changes can cause pressure Organisms unable to adapt quickly enough will die Organisms that adapt are able to pass on their successful traits to future generations Natural Selection Theory Isolation If one portion of a population is separated from another portion then a new species may evolve Natural Selection Theory Mechanisms for population change Key to change is variation among the individuals in the population Individuals are unique due to their genes Genetics Genetics Nucleic Acids Huge molecules that hold information DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid that holds all the genetic information for organisms ghr.nlm.nih.gov DNA Genetic code of all living things Complete set of blueprints and operating instructions for assembling and managing one particular kind of organism Has four basic building blocks Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) DNA A and T can only bond with each other G and C can only bond with each other When four bases bond together in a long chain they form a double helix (ladder) Typical DNA molecule may be about 5 cm long DNA DNA found in the nucleus of the cell DNA is coiled into a compact structure called a chromosome Every cell in every plant and animal has a completed set of chromosomes that define the organism Every time the cell divides to produce two daughter cells the complete set of chromosomes is produced Chromosome, Gene, DNA www.phoenix5.org Genes determine traits Genes: are the units of heredity that is a sequence of bases (A,T,G,C) that give instructions on how to assemble a certain protein Genes are the sugars, phosphates, and bases along the DNA strand in the chromosome The proteins go to the cells to make things such as fats, bone, muscle, nerves, and everything else in a living organism Alleles www.monteweston.com Alleles Each gene has two copies which are called the alleles. (2 alleles= 1 gene) Dominant allele the allele that controls what will happen or which trait will be exhibited (Capital Letter) Recessive allele the allele that is “overruled” and this trait or function will not be seen because of the dominant allele (Lower case letter). Punnett Squares A technique for predicting the characteristics of offspring Example of Punnett Square Punnett Square Always put the dominant allele (G) before the recessive allele (g) so you would write Gg Results: One homozygous dominant (GG) Two heterozygous (Gg) One homozygous recessive (gg) . u w i n n i p e g . c Discovery of Heredity a Gregor Mendel Scientist pioneer to work with pea plants to show how a species can exhibit certain characteristics from one generation to the next. history.nih.gov He was the scientist to support the idea of dominant (capital letter) and recessive (lower case letter) traits. kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca Genotype Genotype Genotype is the genetic makeup of the organism (genes/letters) Example: (letters represent trait…color in this case) Pea flower color B=dominant allele (purple), b=recessive allele (white) A purple offspring would have either a BB or Bb genotype A white offspring would only have a bb genotype www.eastbaymom.com Phenotype Phenotype: how the organisms looks (trait/picture) Example: purple flower, white flower, tall plant, short plant Inheritance Inheritance is passing genetic information from one generation to the next You inherited alleles from your parents