* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download russell-silver syndrome
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
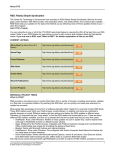
M OLECULAR G ENETICS L ABORATORY , H OSPITAL R USSELL -S ILVER FOR SYNDROME The main feature of Russell-Silver syndrome (RSS) is low birth weight followed by continued growth delays after birth. Individuals with RSS typically have proportionately short stature and normal head circumference. Certain characteristic facial features may also be present (triangular face, down-turned angles of the mouth, prominent forehead, prominent nasal bridge and a small jaw). Other variable features may be seen in children with RSS (see For More Information). Some individuals with RSS will have many of the possible characteristics associated with RSS while others will have very few. G ENETICS T EST M ETHODS RSS is a complex multigenic disorder caused by abnormalities in different genetic regions: Methylation status: Methylation-specific Multiplex-Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MS-MLPA) is used to determine the methylation status of H19. In ~35% of RSS patients the cause is alterations in an imprinted growth regulatory gene, H19, on chromosome 11p15.5. Imprinting: Most autosomal genes are expressed (turned on) in both the paternally and maternally inherited gene copies. Imprinted genes are different in that they are expressed (turned on) in a parent of origin specific manner. H19 works to suppress or hold back growth. Usually, the maternal copy of H19 is expressed (on) and the paternal copy of H19 is methylated (off). Individuals with RSS due to H19 abnormalities have both the maternal AND paternal copies of H19 expressed (both on). In ~10% of RSS patients the cause is uniparental disomy (UPD) of chromosome 7. Patients with RSS due to UPD have two copies of chromosome 7 from their mother and no chromosome 7 from their father. In a small number of RSS patients other gene changes on chromosome 7 or the chromosome 11p15.5 region are found. Some of these are changes in gene copy numbers (duplications) or larger chromosomal rearrangements. S ICK C HILDREN Gene Dosage Analysis: MLPA is used to determine the relative copy numbers of several genes in the 11p15.5 region. Microsatellite analysis for UPD: A PCRbased microsatellite assay is used to compare the genetic material contributed from each parent on chromosome 7. Parental samples are required. W HO S HOULD BE T ESTED ? Individuals suspected of having RSS. Fetuses at risk of having RSS (e.g. intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), positive family history of RSS). T EST SENSITIVITY There are several molecular alterations associated with RSS. Testing with MLPA of 11p15.5 and UPD7 will detect about 49% of RSS patients. See the chart below for details. etiologic heterogeneity in Rss MLPA Testing of 11p15.5: Copy number (11p15.5 region) Methylation Status of Freq. H19 KCNQ10T1 Hypomethylation H19 Normal Hypo Normal 35% Maternal duplication 11p15.5 Abnormal Hypo* Hyper* ~4% UPD Chromosome 7 Testing: Frequency Maternal UPD 7** ~10% For More Information The MAGIC foundation—http:// www.magicfoundation.org/www/ docs/112/russel-silver-syndrome GeneTests online clinical information resource - http:// www.genetests.org/profiles/rss To locate a genetics center near you, please visit the Canadian Association of Genetic Counsellors website at www.cagc-accg.ca or the National Society of Genetic Counselors website at www.nsgc.org 1. Some cases of RSS may warrant a cytogenetic analysis to detect chromosome translocations . 2. Parental samples required for UPD7 testing. are 3. A negative molecular test result does not rule out the diagnosis of RSS. 4. These tests were developed and its performance characteristics validated by the Molecular Genetics Laboratory at the Hospital for Sick Children. It has not been cleared or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The FDA has determined that such clearance or approval is not necessary. This test is used for clinical purposes. *Depends on the extent of the duplication. **MLPA analysis of 11p15.5 will be normal if maternal UPD7 is detected. OMG1620AG/01