* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS!
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
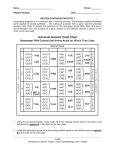
CLASS COPY CLASS COPY CLASS COPY CLASS COPY Simulating Protein Synthesis to create a CHNOPS! Read the following to help you complete a successful CHNOPS organism. Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics such as hair color and blood type. Genes consist of DNA molecules that code for the proteins our cells make. The sequence of nucleotides (and therefore the sequence of bases) in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins. During transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) nucleotides read and copy the DNA sequence into a single RNA strand. mRNA can leave the nucleus because it is single stranded. mRNA travels to the ribosome where proteins are made. The codons in the mRNA strand will pair up with anticodons on the transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Each tRNA has an amino acid. These amino acids are linked together in the same order that their corresponding tRNAs match the mRNA. The process in which the original DNA information (carried by the mRNA) is transferred into a protein is called translation. NEWS FLASH! A meteor has landed on the northern tip of Greenland. When officials went to investigate tiny eggs were found around the meteor site. The eggs were tested and found to contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus and Sulfur, so they were called CHNOPS. A sample of DNA was taken from the organism inside each egg and scientists were able to predict what some of the traits of this “alien” organism might look like. You will use these traits to predict what will hatch from the eggs by drawing a baby CHNOPS. What is a CHNOPS? What does a baby CHNOPS look like? Well, that’s for you to show us! Name: _______________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ CHNOPS A Transcribe and translate the following DNA codes to find out what characteristics your CHNOPS has. Use the charts provided to determine the amino acid sequence and the protein traits of your CHNOPS. FIRST, transcribe the mRNA and use your codon chart to write down the name of the amino acid. SECOND, translate to tRNA and use your anticodons to find the amino acid # on your chart. THIRD, use the numbers to find the trait of your baby CHNOPS Once you have determined the traits of your CHNOPS, build a model to show the class what it looks like. Then answer the questions on the back of this sheet. Gene A DNA: ACC GGT TAT Gene B DNA: AGC CGA Gene C DNA: TTT AAC mRNA ________________ mRNA _______________ mRNA _______________ amino acid amino acid _________________ amino acid _________________ ________________ tRNA _________________ tRNA ________________ tRNA _______________ amino amino acid #________________________ acid #________________________ amino acid #______________________ Trait __________________ Trait _________________ Trait ________________ Gene D DNA: GGA CGC CGA Gene E DNA: GGG AGG AAA CCC Gene F DNA: ATC ATC CTA mRNA ________________ mRNA _______________ mRNA _______________ amino acid amino acid _________________ amino acid _________________ ________________ tRNA _________________ tRNA ________________ tRNA _______________ amino amino acid #________________________ acid #________________________ amino acid #______________________ Trait __________________ Trait _________________ Trait ________________ Name: _______________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ CHNOPS B Transcribe and translate the following DNA codes to find out what characteristics your CHNOPS has. Use the charts provided to determine the amino acid sequence and the protein traits of your CHNOPS. FIRST, transcribe the mRNA and use your codon chart to write down the name of the amino acid. SECOND, translate to tRNA and use your anticodons to find the amino acid # on your chart. THIRD, use the numbers to find the trait of your baby CHNOPS Once you have determined the traits of your CHNOPS, build a model to show the class what it looks like. Then answer the questions on the back of this sheet. Gene A DNA: ACC GGT TAT Gene B DNA: AGC CGA Gene C DNA: TTT AAA mRNA ________________ mRNA _______________ mRNA _______________ amino acid amino acid _________________ amino acid _________________ ________________ tRNA _________________ tRNA ________________ tRNA _______________ amino amino acid #________________________ acid #________________________ amino acid #______________________ Trait __________________ Trait _________________ Trait ________________ Gene D DNA: GGA CGC CGC Gene E DNA: GGT AGG AAA CCC Gene F DNA: ATC ATC AAT mRNA ________________ mRNA _______________ mRNA _______________ amino acid amino acid _________________ amino acid _________________ ________________ tRNA _________________ tRNA ________________ tRNA _______________ amino amino acid #________________________ acid #________________________ amino acid #______________________ Trait __________________ Trait _________________ Trait ________________ Name: _______________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ CHNOPS C Transcribe and translate the following DNA codes to find out what characteristics your CHNOPS has. Use the charts provided to determine the amino acid sequence and the protein traits of your CHNOPS. FIRST, transcribe the mRNA and use your codon chart to write down the name of the amino acid. SECOND, translate to tRNA and use your anticodons to find the amino acid # on your chart. THIRD, use the numbers to find the trait of your baby CHNOPS Once you have determined the traits of your CHNOPS, build a model to show the class what it looks like. Then answer the questions on the back of this sheet. Gene A DNA: ACC GGA TAT Gene B DNA: AGC CGA Gene C DNA: TTT AAC mRNA ________________ mRNA _______________ mRNA _______________ amino acid amino acid _________________ amino acid _________________ ________________ tRNA _________________ tRNA ________________ tRNA _______________ amino amino acid #________________________ acid #________________________ amino acid #______________________ Trait __________________ Trait _________________ Trait ________________ Gene D DNA: GGA CGC CGC Gene E DNA: GGT AGG AAA CCC Gene F DNA: ATC ATC CTA mRNA ________________ mRNA _______________ mRNA _______________ amino acid amino acid _________________ amino acid _________________ ________________ tRNA _________________ tRNA ________________ tRNA _______________ amino amino acid #________________________ acid #________________________ amino acid #______________________ Trait __________________ Trait _________________ Trait ________________ Analysis Questions: 1. Why do you think this organism was called a “CHNOPS” _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 2. Distinguish between transcription and translation What is the product of each? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 3. Where do transcription and translation occur in a cell? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 4. How many tRNA nucleotides form the anticodon that attaches to the mRNA?___________________ Critical Thinking: 1. If you knew the make-up of a protein (the amino acid sequence), how would you determine the DNA code for that protein? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 2. How would a single change in the DNA nucleotide base alter the formation of a protein – what might happen? _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ tRNA Triplet ACC AGC CGA AAC CGC GGG AGG AAA UUU GGU UAU CCC AUC CUA GGA AAU Amino Acid Sequence 20-11-13 20-12-13 16-2 12-7-8-1 5-7-8-1 9-8 9-4 11-3-2 11-3-3 6-6-10 6-6-14 Amino Acid Number 20 16 2 4 3 5 7 8 9 12 13 1 6 10 11 14 Trait BLACK SPOTS BLUE SPOTS ____ FOUR LIMBS LONG TAIL HORNS CURLY HAIR STRAIGHT HAIR RED SKIN GREEN SKIN ELONGATED BODY SPHERE SHAPED BODY