* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HERE
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
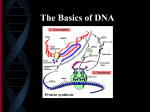
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis DNA has the code to make proteins • DNA contains the instructions for the cell: – It tells it how to make copies of cells: • Body (somatic) cells are copied by mitosis • Sex cells are copied by meiosis – It tells it how to make proteins which have many functions in the cytoplasm of the cell. Proteins are important • Proteins make up genes, which determine your genetic traits (hair color, height, etc.) • Proteins act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. • Proteins direct the chemical reactions in your cells and “tell the cell organelles” what to do. • IN SUMMARY – Proteins are the instructions of the DNA in action. DNA review • Nucleic acids are made up of monomers of units called nucleotides: Sugar, phosphate and base • • • • • DNA sugar is DEOXYRIBOSE There are two strands in DNA (the two sides) The bases in DNA are : A,T,C,G AG are purines, CG are pyrimidines DNA NEVER LEAVES THE NUCLEUS RNA is a little different • RNA is a single strand • R stands for RIBOSE which is the sugar. • There are two kinds of RNA: – mRNA which is formed in the nucleus – tRNA which is in the cytoplasm • The bases of RNA are : C,G and A, U (not T) • mRNA LEAVES the nucleus and goes to the ribosome where protein synthesis occurs. Protein synthesis is a series of STEPS • 1. mRNA gets instructions from DNA – This is called TRANSCRIPTION • 2. mRNA leaves the nucleus and takes the instructions to the ribosome. • 3. mRNA gives the message to the t RNA – This is called TRANSLATION The tRNA attaches AMINO ACIDS together to FORM PROTEINS – This is called Protein Synthesis • 4. PROTEINS coil up to form shapes that can act as enzymes and bond with substrates. STEP 1 – called TRANSCRIPTION A. DNA uncoils when an enzyme tells the DNA to unwind. This creates a REPLICATION FORK B. The RNA POLYMERASE puts the mRNA nucleotides together along the DNA strands, adding the complementary bases and proofreading them. Step ONE Step 2 • mRNA leaves the nucleus and takes the instructions to the ribosome. Step 2 Step 3 A. mRNA gives the message to the t RNA This is called TRANSLATION B. The tRNA carries Amino Acids on it (every 3 bases on tRNA has an amino acid attached these are called CODONS) C. The tRNA attaches AMINO ACIDS together to FORM PROTEINS This is called Protein Synthesis TRANSLATION tRNA with amino acid attached Protein formed from amino acids mRNA template Step 4: The Protein then coils up The protein then can do its job • Like catalyze (speed up) reactions when acting as an enzyme: products Reactant Substrate Enzyme Catalyst ACTIVE SITE THE “CODE” • The code for the tRNA to use to attach the amino acids together into the protein strand is found on the mRNA base sequence. • Three bases make up the base sequence. • The three bases are called the CODON. • Scientists use tables to determine the correct match of codon to amino acids. • There are 21 amino acids in the body. Table found in Ch. 10 Second nucleotide Another type of codon table