* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biol 178 Lecture 6
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
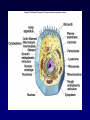
Bio 178 Lecture 6 Cell Structure Sui Huang and Donald E. Ingber, http://w3.mit.edu/i-m/image2big.htm Reading • Chapter 5 Quiz Material • Questions on P 104 • Chapter 5 Quiz on Text Website (www.mhhe.com/raven7) Outline • Characteristics of cells • Microscopy Characteristics of All Cells 1. Hereditary Material • Prokaryotes Nucleoid - DNA not surrounded by a membrane. • Eukaryotes Nucleus - DNA is surrounded by the nuclear envelope. 2. Cytoplasm Cell matrix. Characteristics of All Cells 3. Phosopholipid Bilayer boundary Plasma membrane is 5-10 nm thick and contains embedded proteins. Modern Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. A cell is the smallest living entity. 3. New cells arise only via division of pre-existing cells. Schleiden Schwann Cell Size Most eukaryotic cells are 5-20 µm Reasons • Surface to Volume Ratio 1. Cells need a large a S:V to allow transport of nutrients, gases, & waste across the plasma membrane. 2. Much easier to achieve if an organism is made of numerous small cells rather than few large cells. • One Command Center per Cell The nucleus can more easily provide for the cell if the cell is small. Cell Size How do large cells overcome these problems? • Syncytium Skeletal Muscle http://www8.nos.noaa.gov/coris_glossary/index.aspx?letter=s Cell Size How do large cells overcome these problems? • Syncytium (cntd.) Soybeet syncytium induced by nematode parasite Heterodera glycines. http://www.apsnet.org/education/IllustratedGlossary/PhotosSV/syncytium.htm Cell Size How do large cells overcome these problems? • Cell Shape http://www.nature.com/news/2004/040531/images/nerve_180.jpg http://web.sfn.org/content/Publications/BrainBackgrounders/communicat ion.htm Cell Size How do large cells overcome these problems? • Large Nuclei ES gland of Otostrongylus circumlitus (copyright J. Elson-Riggins) Microscopy Resolution The minimum distance between 2 points at which they can be distinguished as separate objects. Human Eye: ~ 100 µm Light Microscope: 0.2 µm (in theory) Electron Microscope: 0.1 nm Microscopy Resolution (R) R = 0.61 n sin = 1/2 angular width cone of light rays collected by objective lens n = refractive index of medium separating object from objective and condenser lenses = wavelength What limits the resolution of the light microscope? William H. Heidcamp, http://homepages.gac.edu/~cellab/chpts/chpt1/figure1-3.html LM of O. circumlitus Anterior End Copyright J. Elson-Riggins Electron Microscope Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) Electrons are transmitted through the specimen (thin section). http://euch3i.chem.emory.edu/~nmr/apk/inst rumentation.html (light) = 0.53 µm http://www.barrettresearch.ca/teaching/ nanotechnology/nano02.htm (electrons) = 0.004 nm TEM (O. circumlitus ES Gland) Copyright J. Elson-Riggins Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Electrons are reflected off the surface of the specimen gives 3D images. Ant head http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/esem/gallery.html Staining Specimens for Microscopy Staining increases contrast (cells are 70% water little to impede passage of light rays/electrons). O. Circumlitus ES gland stained with PAS and aniline blue-black. Specific stains are used to visualize structures. Copyright J. Elson-Riggins Staining Specimens for Microscopy Immunocytochemistry Antibodies are labeled with fluorescent molecules (or other substances) and used to stain specific structures. Squamous carcinoma cells. Blue = Nuclei, Red = Cytoplasm, Green = Plasma membrane NANCY KEDERSHA / IMMUNOGEN / SCIENCE PHOTO, LIBRARY http://www.sciencephoto.com/images/imagePopUpDetails.html?id=771320363 Characteristics of Principle Cell Types 2 structurally different types of cells: PROKARYOTE True Nucleus? Membrane bound organelles? Kingdoms EUKARYOTE