* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE NORMAL METABOLISM OF PHENYLALANINE (pathways a
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
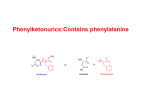
PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) FACT SHEET THE NORMAL METABOLISM OF PHENYLALANINE (pathways a and b) AND THE ABNORMAL METABOLISM IN PHENYLKETONURIC SUBJECTS (pathway c) HYDROXYPHENYLACETIC ACID Dietry sources, particularly plant proteins BREAKDOWN (c) PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE PHENYLALANINE* (a) TYROSINE (c) (b) PHENYLACETIC ACID* BODY PROTEINS *Agents, thought to be responsible for mental retardation, which accumulate in phenylketonuric subjects (PKU). These are broken down into ketone bodies which appear in the urine. Other symptoms include skin lesions. Test Ferric chloride + urine of new born baby Green colour in the presence of ketone bodies. Treatment A strictly controlled phenylalanine low diet must be followed for life. No protein rich foods (e.g. meat, eggs, pulses). No aspartame sweetner. As phenylalanine is itself an essential amino acid small doses must be supplied. Other nutrients may need supplementing. Frequency 1 in 10 000 in Caucasians of NW Europe Causes 1. A single mutant recessive allele of the Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH) gene. This results in the inability to produce the enzyme. Locus: Long arm of Chromosome 12. 2. Dietary excess of plant proteins which results in the exhaustion of a protein cofactor (pterin) needed by the enzyme. Evolution Heterozygotes (carriers) are thought to be less susceptible to toxins produced by the moulds Aspergillus and Penecillium. These grow on foods in damp wet climates (e.g. NW Europe). Heterozygous women show lower spontaneous abortion rates. 14/05/2017