* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11: Gene Expression
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
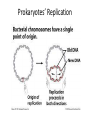
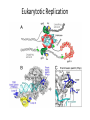
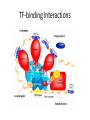
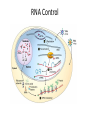
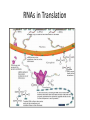
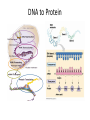
Gene Expression Control in Division & Development Prokaryotes’ Replication Prokaryotes’ Transcription • 1965 Nobel Prize to Jacob & Monod for work on lac operon in E. coli • Lactose is metabolized by 3 enzymes in E. coli • Genes for these proteins are sequential • An operator sits between promoter & these structural genes • lac operon = promoter + operator + 3 genes • Upstream regulatory gene codes for repressor lac operon http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/lacoperon/ regulate.html How it works. • Regulatory gene codes for repressor protein • Repressor protein binds to the operator site • Repressor prevents RNA polymerase advancement from its promoter site • Repressor protein selectively binds lactose & cannot bind the operator site then • Repression is lifted genes are “turned on” only when lactose is present Eukaryotic Replication Eukarytotic Replication Transcriptional Control • Transcription factors (TF) bind to regulatory elements on DNA, proteins, & other TF – Promoters – Enhancers – Repressors • TF recruit RNA polymerase to promoter • TF-to-TF binding can change shape of DNA TF-binding Interactions Eukaryotic control • Control is at level of individual chromosome • Euchromatin, uncoiled DNA, is site of active transcription • DNA contains bases that code for proteins (exons) & bases that do not (introns) • Exons & introns are both transcribed • Only exons are translated • Introns may serve as regulatory elements Transcription to Translation Transcriptional Control • Pre-mRNA is full copy of DNA gene’s message • Splicesomes (RNA + protein) cut out introns & fuse exons; ribozymes (RNA) also splice • Introns regulate RNA, bind to &/ or control expression (or maybe do nothing at all) • Exons can code for functional domains • Exons can be selected to form specific protein RNA Control RNAs in Translation DNA to Protein Recombinant DNA (rDNA) • Insert genes from 1 organism to another – Clone the DNA segment • Use restriction enzymes to cut out gene • Use the same enzyme to cut vector’s DNA – Viruses or plasmids (ringed DNA in bacteria) • Incubate DNAs & DNA ligase to reconnect • Inject recombinant plasmid into host bacteria • Bacteria now will produce the new protein Recombinant DNA Genes for Development • Cells differentiate to become specialized – Every zygote has all the DNA – Cells/ tissue specialize in morphogenesis – Cells only express DNA for their functions • Homeotic genes dictate loci of anatomy – Specific sequence within gene = “homeobox” • Homeotic genes form regulatory proteins – Control which genes are expressed – Control rates of cell division & gene expression Cancer & Cell Control • Proto-oncogenes control normal cell division, growth, & behavior • Carcinogen = mutagen DNA damage • Mutated proto-oncogenes “oncogene” • Oncogenes promote uncontrolled growth tumors (benign or malignant) cancer • Metastasis = spread of CA beyond origin • Mutated tumor-suppressor genes cancer – Mutations in all 3 tumor-suppressor genes + viral oncogene + mutated proto-oncogene Types of Cancer • Carcinomas – Skin & tissues lining organs • Sarcomas – Bone & muscle • Lymphomas – Lymphatic system’s solid tumors • Leukemia – Blood-forming tissues uncontrolled WBC production