* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anchorage, cell density, and chemical growth factors affect cell
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
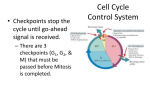
Anchorage, cell density, and chemical growth factors affect cell division Animals and plants need to be able to control the timing of the cell division in different parts of the body in order to grow and develop normally. EX. Cells in the digestive tract and skins cells need to be replaced frequently to replace cells that have flaked off. Liver cells usually do not divide unless the liver is damaged. -Most animal cells exhibit anchorage dependence – they must be in contact with a solid surface to divide. Scientist have found that cells growing on the surface of a dish multiply to form single layer and usually stop dividing when they tough one another (density-dependent inhibition). If cells are removed – the cells bordering the open space begin to divide again. Clearing a space in a dish is analogous to cutting your skin. What causes this??? Proteins called growth factors – proteins that are secreted by certain body cells to divide. Most cells require growth factors to start dividing and they stop dividing when they run out of these substances. Growth factors signal cell cycle control system -Cells do not divide unless they are signaled by other cells to do so. Growth factors are the main signal. -The events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system (it is a set of molecules in the cell that both trigger and coordinate key events in the cycle). Ex. Within the M phase – metaphase does not automatically lead to anaphase. Proteins of the cell cycle control system must trigger the separation of sister chromatids. -There are checkpoints in the cell cycle. There are three major check points during G1, G2 and M phase. Signals within the cell, detected by the control system, tell whether key cellular processes have been completed before the cycle moves on. The system also receives messages from outside the cell – indicating both general environmental conditions and the presence of specific signal molecules from other cells. G1 – receives the go-ahead signal from a growth factor and enters S phase. If this happens the cell will usually complete its cycle and divide. If it does not receive the signal to go-ahead it enters G0 (nondividing state). Nerve cells and muscle cells are in G0 phase. CANCER Cancer cells do not respond normally to the cell cycle control system – they divide excessively and can invade other tissues of the body. Cancer begins: -single cell goes under a transformation (process in which a normal cell converts to a cancer cell) -Body’s immune system normally recognizes a transformed cell and destroys it. -If the cell escapes destruction it may grow to a tumor (abnormally growing mass of body cells) -If the cells (tumor) remains at the original site – the tumor is called benign. They can cause problems if they grow in and disrupt certain organs. -A malignant tumor can spread into neighboring tissues and other parts of the body. Cancer cells may separate from the original tumor or secrete signal molecules that cause blood vessels to grow toward the tumor. A few tumor cells may enter the blood and lymph vessels and move to other parts of the body where they from new tumors. Metastasis is when the cancer cells spread through the circulatory system beyond the original site. **Cancers are named according to organ or tissue in which they originate.** **Four categories of Cancer 1. Carcinomas – cancer that originates in the external or internal coverings of the body (skin or lining of the intestines) 2. Sarcomas – cancers in the tissues that support the body (bone and muscle) 3 + 4. Leukemias and Lymphomas – cancer of the blood-forming tissues (bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes) Cancers do not have the normal signals that regulate the cell cycle. They continue to divide even at high densities. Many cancer cells have defective cell cycle control systems that proceed past checkpoints even in the absence of growth factors. Other cancers themselves make growth factors that make them divide continuously. If a cancer cell does stop dividing it is random and not at the checkpoints. Cancer cells seem to be “immortal” – they keep dividing.