* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve cells - WordPress.com
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
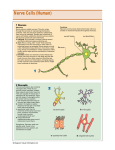
Presenter: Romario Dixon Types of Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue consists of two main types of cells: neurons and neuroglia. Nerve cells, or neurones(also written "neurons") transmit nerve impulses that move information around the body. Neuroglia are also known simply as "glia" and have various functions in support of nerve cells but do not transmit nerve impulses themselves. More information about both of these types of cells follows Neurons Neurones (nerve cells) are sensitive to various types of stimuli such as heat/cold, light/dark, pressure. They transmit electrical nerve impulses thereby moving information around the body. The structure of a neurone Neuroglia / Glia Neuroglia are sometimes known as simply "Glia". They are not sensitive to stimuli and so do not generate or conduct nerve impulses. "Glia" or "Neuroglia" are therefore sometimes referred to as the "non-nervous cells of the nervous system". Their functions within the nervous system depend on the specific type of neuroglia Types of Neuroglial Cell: Astroglial Cell Astrocyte Structure: An astrocyte is a star-shaped cell that has many processes extending from its cell body into the surrounding network of nerve fibres. Function(s): Supply of nutrients to neurons. Removes excess neurotransmitters Maintains appropriate balance of Ca2+ and K+ ions (which are important in passing nerve impulses at synapses). Helps migration of neurons during brain development. Aids formation of the blood-brain barrier. (Possibly participating in information storage processes) Ependymal Cell Ependymal cells are found in the Central Nervous System (CNS), that is in the tissues of the Brain and Spinal Cord. Function(s): Protection: Forms lining of the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord. Forms cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Aids circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Ependymal cells form the extremely thin membrane called the ependyma that lines the ventricles of the brain and choroid plexuses Ependymal Cell Structure: Microglial Cell Microglial cells are sometimes known simply as "microglia" and are found in the Central Nervous System (CNS), that is in the tissues of the Brain and Spinal Cord. Structure: Microglia are small glial cells. Function(s): Protects CNS neurons from disease e.g. by clearing away debris and dead cells. Therefore some texts describe microglia has having a "mainly scavenging" function. Microglia may be compared with macrophages (which are large scavenger cells, not specific to the nervous system). A video of the structure and function of nerve cells C:\Users\120024\Desktop\Neurons.htm