* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download For patients with a suspected diagnosis of familial adenomatous
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
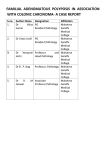
COLARIS AP® – SAMPLE LMN #4 For patients with a suspected diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis 20-99 colorectal adenomatous polyps [Date] ATTN: [Physician Name, M.D.] [Insurance Company/Institution] [Street Address] [City, State, Zip] Re: [Patient Name or ID/Claim Number] Dear Medical Director: I am writing to request coverage for analysis of the APC and MYH genes for __________________________________________________due to a personal history of ________________________________________________________ diagnosed at age(s) ______________________________. Additional family history includes: Relationship___________________ Cancer or Adenoma ___________ Age____ Relationship___________________ Cancer or Adenoma ___________ Age____ Relationship___________________ Cancer or Adenoma ___________ Age____ The number of adenomatous colorectal polyps detected in this patient (##) thus far is suggestive of mutations in the APC and MYH genes. Mutations in the APC gene are responsible for Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP), which is characterized by a proliferation of adenomatous polyps throughout the colon and rectum. The clinical features of some individuals and families with mutations in the APC gene can be less dramatic (fewer numbers of polyps, later age of polyp onset, etc.). Therefore, the number of adenomatous colorectal polyps detected in this patient (##) thus far, is suggestive of a mutation in the APC gene. Carriers of APC mutations have a greater than 90% chance of colorectal cancer before age 50 unless a prophylactic colectomy is performed. Individuals who carry an APC gene mutation also are at significant risk to develop extracolonic cancers following prophylactic colectomy. The risk of an extracolonic cancer in individuals with FAP is 11% by age 50 and 52% by age 75. These risks warrant specific screening for cancers rarely seen in the general population including duodenal cancer. Biallelic mutations in the MYH gene are associated with the presence of multiple colorectal adenomas and cancer. In addition, patients may present with extracolonic disease similar to patients with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), including duodenal polyposis. Current medical management recommendations suggest that individuals who have inherited two mutations in the MYH gene be managed similarly to individuals who carry an APC gene mutation, including frequent colonoscopies and upper GI endoscopy, with the option of colectomy. Based on the above stated cancer risks and the aggressive surgical and screening recommendations that result from these risks, I am recommending genetic testing for mutations in the APC and MYH genes to confirm a diagnosis of polyposis. The information gained from genetic testing will have a significant impact on both the patients’ short- and long-term medical management. [include as appropriate] According to the American Gastroenterological Association Medical Position Statement, APC gene testing is “the screening test of choice” and is indicated for “those 10 years or older at risk for FAP” (AGA Position Statement, Gastroenterology 121:195-197, 2001). These guidelines also state that screening of the colon and rectum for polyps should begin approximately at age 10. Therefore, genetic testing of at-risk family members is recommended by 8-12 years of age. The information gained from genetic testing will therefore likely have a significant impact on the patient’s short- and long-term medical management. A negative genetic test in the relative of a known mutation carrier can alleviate the need for annual lifetime surveillance (sigmoidoscopy) commencing in childhood. Myriad Genetic Laboratories performs comprehensive analysis of the APC and MYH genes. Sequence analysis is the most sensitive clinical test to look for predisposition mutations and is one of the most complex clinical diagnostic tests that exists today. The technical challenge of traditional DNA analysis represented as "usual and customary" should not apply to the complex analysis involved with APC and MYH analysis. Thank you for your consideration of this case. Please feel free to contact me directly if I can be of any further assistance in your decision for coverage. Sincerely, [Physician Signature]