* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules and SPF groups
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
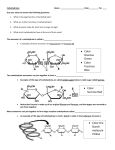
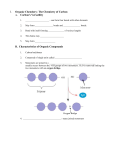
Macromolecules – 4 classes, monomers, S.P.F, Macromolecules Monomers Bonds Functions Carbohydrates (Polysaccharide) Saccharides 1-4 Glycoside Lineage Carbohydrates in general provide and store energy in animals, plants and bacteria. Proteins (Polypeptide) Amino Acids (20 types) Peptide Most Important, for building or growth, and repair. *Enzymes Provide energy Nucleic Acid (DNA & RNA) Nucleotides (A, T, C, G, U) 3 – 5 prime bonding Coding for proteins, adding atoms so we don’t die Carbohydrates: Starch – Alpha Glucose they are also geometric isomers. They provide most energy to this in the planet; every culture based their food on starch. Cellulose - Beta Glucose are geometric isomers. Humans cannot digest cellulose. Plants use it for their structure like cell walls. Protein: Enzymes – Controls the rate of decaying in anything and everything Nucleic Acid: D.N.A – Adds Deoxy to help live longer and slow the rate Water & its properties S.P.F Hydroxyls – (OH-), It makes the thing basic & polar making it hydrophilic Carbonyl – R-C=0-R or H, Ketones or Aldehyde, Carboxyl (R-C=OH) Makes things basic Makes it acidic and polar (Carboxyl) Amine – NH2, makes things Makes water 23AA = 22water basic e.g. glycine amino acids molecules is Amine + Carboxyl Sulfhydryl – SH, SH – SH = Disulfide bridge cross linking stuff such as hair Phosphate - PO4 = makes energy, and makes it polar by being negative Methyl Group – CH2, biological marker, the more methylated a gene is the less expressed it is. Methylate and DE methylate to control expression Dehydration/ condensation – remove H2O out of 2 monomers to make them bond. Catabolic – Depolymerize take/ break down (hydrolysis) Anabolic – Polymerize make (condensate) Enzymes are biological catalysts that have an active sight that fits a specific substrate. The structure and therefore function of an enzyme are controlled by the environment, can denature and renature these active sight. Amylase – Breaks down Starch