* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Rosetta@home wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein design wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
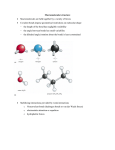
• Proteins • Protein Structures and Shapes • Protein Functions Protein Structures and Shapes • • • • • • Amino acids Peptide bonds alpha helix and beta sheet Domains and Modules Classification of Families Protein Assembly Amino Acids form polypeptide through peptide bond Structural Components of a protein The 20 Amino Acids 2 negative, 3 positive, 5 non-charged polar, 10 nonpolar Read Page 132-133, panel 3-1 Limitations on the bond angles Ramachandran plot Four major noncovalent bonds that help protein folding 1. Ionic bond 2. van der Waals 3. Hydrogen bond, 4. Hydrophobic force Hydrophobic “forces” The importance of hydrogen bond Folding and Refolding Secondary structures a helix and b sheet Coiled-coil structure a-keratin Two types of b sheet structures Src Kinase The combination of ahelix and b-sheets Classification of protein families Two serine proteases Two homeodomains from different species (yeast a2, green; drosophila engrailed protein, red) Domains and Modules Domain shuffling Calcium binding domain Kringle domain Module Examples The combination of Modules Design Strategy ECFP(1-227) SH2(from c-Src) Linker Substrate EYFP 433 nm Weak FRET 433 nm Strong FRET 527 nm Src Activation Phosphatase 490 nm Protein Subunits Hydrophobic forces Hemoglobin Protein assemblies Actin Filaments Disulfide bonds Extracellular matrix protein are covalently cross-linked by Disulfide bonds Hexagonally packed globular protein subunits can form flat sheets Self-Assembly Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) Model Structure Electron Micrograph The formation of Virus shell X-Ray Crystallography of different virus (A) Tomato bushy stunt virus (B) poliovirus (C) simian virus 40 (SV40) (D) satellite tobacco necrosis virus Three mechanisms of length determination for self-assembly Protein assembly aided by assembly factors (insulin assembly) Protein Functions • • • • • • • • • Protein Binding Protein conformation Antibody Enzyme and substrate Catalytic Reaction Kinase and phosphatase GTPase, GEF, GAP Motor protein Membrane-bound protein Protein binding Protein binding sites Protein binding site Cyclic AMP Protein binding sites 1. Restriction of water entrance 2. Alteration of reactivity Sequence Comparison to find conserved binding sites Sh2 domain Three ways for two proteins to bind Antibody Noncovalent bonds and protein interactions Binding Energy and Equilibrium constant Enzyme Kinetics Read Panel 3-3, page 165 Enzymes lower the activation energy to accelerate chemical reactions Lysozyme actions Bending of the polysaccharide bond Steps of lysozyme actions Strategies of enzyme catalysis Feedback inhibitions Coupled regulation: Positive Regulations Coupled regulation: negative Regulations Coupled regulation on multiple subunits Aspartate transcarbamoylase Kinase and phosphatase Kinase Domain Kinase families Cyclin-dependent Kinase (CdK): Signal integrator threonine tyrosine Src Kinase Multiple Inputs for Src Kinase activation GTPases Ras Structure: One kind of GTPases Phosphorylation and GTP binding regulations EF-Tu and its regulation of tRNA Motor Protein Regulation Myosin on Actin and Kinesin on Microtubules Membrane Protein Calcium Pump on Sarcoplasmic reticulum

















































































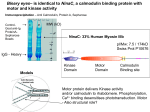






![c stands for c ellular [as opposed to v iral genes]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017443238_1-c2172f0d7f0ce117d9b392ebaadf62fc-150x150.png)