* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Evolution
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
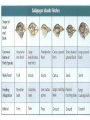
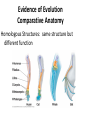
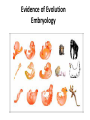
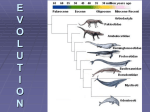
E V O L U T I O N Questions to Ponder TRUE/FALSE 1. You can web your hands if you try. 2. You can acquire traits in your lifetime that will help you survive. 3. All organisms have the same chance for survival. 4. All organisms need the same favorable trait. 5. Evolution of most organisms occurs during their lifetime. THEORIES OF EVOLUTION: LAMARCK VS. DARWIN • Lamarck (1744-1829) • Darwin (1809-1882) LAMARCK’S THEORIES: wrong Lamarck (1744-1829) • Acquired trait: a trait NOT determined by genes, it arises during an organisms lifetime as a result of behavior and can be passed onto offspring WRONGLamarck: Acquired Trait Example: giraffes evolved their long necks by stretching further to get leaves in trees and that this change in body shape was passed on. CHARLES DARWIN (1809-1882) voyage of the Beagle The study of the Galapagos finches led Darwin to his TWO theories… 1) Decent With Modification 2) Natural Selection Darwin’s Theories 1) Descent with Modification • Newer forms appearing in the fossil record are modified descendents of older species • All species had descended from one common ancestor Descent With Modifications - tree of life that links all living things! Modification by Natural Selection Describes how evolution occurs organisms in nature produce more than can survive 1. THEREFORE living things face a constant struggle for existence POPULATIONS HAVE VARIATIONS 2. Variation exists within populations because: - mutation - Crossing Over/Independent Assortment (make different gametes) - Sexual reproduction - Random fusion of two gametes Through mutation three variations of neck length exist: Short, Medium and long necks. Let’s review Mutations SOME VARIATIONS ARE FAVORABLE Having a high number of favorable traits gives the organisms an adaptive advantage 3. Non-random Survival and Reproduction -Individuals with traits best suited to their environment (favorable traits) survive and reproduce in high numbers The long neck giraffe has the “best advantage” and therefore reproduces more than the others 4. These favorable traits have to be heritable (able to be passed down to offspring) - Fitness: organisms ability to survive and pass on its genes SURVIVORS HAVE FAVORABLE TRAITS TO PASS TO OFFSPRING Long neck giraffes have baby long neck giraffes 5. Adaption: The number of organisms with favorable traits increases Populations genetically change to become more suited to the environment The entire population of giraffes now ALL have long necks POPULATIONS CHANGE OVER TIME Summary: • Natural selection is not an active process: the environment “selects” the traits that are favorable and those that are not • If the environment changes, so must the ...population **The environment decides which alleles are favored not the individual** Evidence of Evolution 1) Fossil Record Evidence of Evolution Comparative Anatomy Homologous Structures: same structure but different function Evidence of Evolution Comparative Anatomy Analogous Structure: Same function but different underlying structures Evidence of Evolution Comparative Anatomy Vestigial Structure - body part that is evolutionarily reduced or has no use Evidence of Evolution Embryology Evidence of Evolution Molecular Biology