* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Thirteen Change Over Time
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
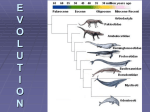
Adaptation: process by which an organism/population becomes better suited for their environment. • Camouflage, Morphology, Behavior, Biochemical • List behavioral adaptations. • Explain the idea of “survival of the fittest” using the term adaptation/adapt. Change Over Time Aka: Evolution Theories of Evolution • Evolution refers to change over time. • Several scientists have contributed to the current theory of evolution. The theory is constantly changing-that is why it is a theory! • Lamarck – Similar species descended from the same ancestor. – First to state that organisms change over time. – Lamarck believed acquired traits were passed on to offspring and that is how species change over time. – Passing of acquired traits was easy to disprove. Who was Charles Darwin? • Trained in the church but studied science. • Took a job on the HMS Beagle as a naturalist traveling to South America and the Galapagos Islands for 5 years. • Noticed finches in different areas had beaks that were suited for the food in that area. Adaptive radiation: because of differences in the environment, many different forms of a speices emerge. • Darwin’s Evidence of Evolution – Similar Structures Homologous Structures: same structure but used for the different function. Ex. Forearm of humans and the wing bones of a bat. Ex. wings of a bird and wings of a bat. – Vestigial Organs • Once very important but now reduced in size and function – Embryology – Fossils • All of these pieces of evidence point to a common ancestor. • Darwin and Wallace – Both proposed that species were changed by natural selection. – The organisms that were best adapted to their environment would survive to reproduce. =fitness – If a trait is favorable, what will happen to that trait in the population? – If a trait is selected against what will happen to that trait? – What will happen to the genes (alleles) associated with these traits? Title: Bear Lab / 3.4/ 40 pts. • Question/Purpose: • Background: Paragraph form. • Read Story • Define evolution. • Answer Background Questions • • • • • Hypothesis: Write a possible answer to the question Draw Data Tables Read procedure!!! Collect Data and Create a graph for the second table. Conclusion • Review how Evolution by Natural Selection Works: – Organisms would grow unlimited if it were not for the environment. – The environment (nature) determines which traits are favorable or not so…The mechanism of evolution is natural selection. – The most “fit” organisms will survive to reproduce and the species will change. Bear Lab / 3.4 / 60 pts. • Day 1 Review • Day 2: • Hypothesis: What will happen to a recessive allele if the environment selects against it? • Data: – – – – Genotype data tables Above the AA and Aa columns write ‘SAD’. Above the aa column write ‘HAPPY’. Collect Data and Graph Table 2 • Conclusion Types of Natural Selection • • • • Stablizing: the average trait is best Disruptive: both extreme traits are best Directional: one extreme trait is best Diagrams. • Which type of selection is shown when insects become resistant to pesticides? MRSA Types of Natural Selection • • • • • Stablizing: the average trait is best Disruptive: both extreme traits are best Directional: one extreme trait is best Diagrams Part B on your Worksheet – 8 minutes. How do organisms evolve so much they make a new species? • Definition of a species: similar organisms that can reproduce to create fertile offspring Making a new species •Requires isolation and evolution in different directions •Isolation can be because of a physical or behavioral barrier. –Physical - geographic isolation. –Behavioral- non-mating because of unrecognizable courtship rituals. • This results in divergent evolution and eventually a new species. How fast does change occur? • Very slowly – Punctuated or gradual • Convergent evolution: Unrelated species evolve similar traits because their environments are the same OR it is a really good trait! • Co-evolution: organisms evolve together – Ex. Flowers and pollinators • Evolution works on genes to change populations of species over time, not on individuals. • What role do genes play???? – If a phenotype is unfavorable in an environment, the genotype for that trait will decrease in the population. (BEAR LAB!!!) • What types of organisms do we use to study populations? • Discovery Video Clip • Question: Do large, colorful tail feathers in male peacocks help the individual to survive or the species? Which is more important? • Sexual Selection – Selection of an individual based on certain traits that are favorable to the opposite sex but not necessarily favorable in the environment. • Artificial Selection-humans decide the favorable traits. Ex. Dog Breeding, Agriculture