* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download photosynthesis-and-cellular-respiration-worksheet
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
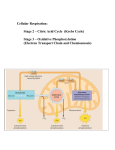
Photosynthesis Worksheet Answers Interactive Question 10.1 a. b. c. d. e. f. Outer chloroplast membrane Granum Inner chloroplast membrane Thylakoid space Thylakoid Stroma Interactive Question 10.2 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. Light H2O Light reactions O2 ATP NADPH CO2 Calvin Cycle G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate) Interactive Question 10.6 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. Photosystem II Chlorophyll a (P680) H2O 1/2O2 Electrons Primary electron acceptor Electron transport chain (ETC) Proton (H+) gradient ATP (by chemiosmosis using ATP synthase) Photosystem I Chlorophyll a (P700) Primary electron acceptor NADP reductase NADPH Interactive Question 10.11 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Carbon fixation Reduction phase Regeneration of starting material 3 CO2 Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) Rubisco (enzyme) 3-phosphoglycerate (3PGA) 1 h. i. j. k. 6 ATP 6 ADP 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (we did not discuss this one) 6 NADPH 6 NADP+ 6 Pi (Pi = inorganic phosphate, meaning a phosphate when it is separated from some carbon compound and is by itself) l. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) m. G3P n. Glucose and other organic molecules o. 3 ATP 3 ADP + 3 Pi Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers Interactive Question 9.1 a. C6H12O6, 6 CO2, ATP (= heat) Interactive Question 9.2 a. Oxidized b. Oxidizing agent c. Reduced Interactive Question 9.3 a. Oxygen b. Glucose c. Some is stored in ATP and some is released as heat Interactive Question 9.4 a. Electron acceptor or oxidizing agent b. NADH Interactive Question 9.5 a. b. c. d. e. f. Glycolysis Kreb’s cycle (citric acid cycle) Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation Substrate-level phosphorylation Substrate-level phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation Interactive Question 9.6 a. 2 ATP b. 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (we did not discuss this G3P at this point of the pathway, but it happens to be the same molecule that we see produced in the calvin cycle) c. 2 NAD+ d. 2 NADH e. 4 ATP (remember a total of 4 ATP are made in glycolysis, but it also requires 2 ATP so the net ATP is 2) f. 2 pyruvate 2 Interactive Question 9.7 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. Pyruvate (from glycolysis) CO2 NADH CoA (coenzyme A) Acetyl CoA Oxaloacetate Citrate CO2 NADH CO2 NADH ATP FADH2 NADH Interactive Question 9.8 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. Intermembrane space Inner mitochondrial membrane Mitochondrial matrix Electron transport chain NADH + H+ NAD+ H+ 2 H+ + 1/2O2 H2O ATP synthase ADP + Pi ATP Interactive Question 9.9 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. -2 4 Kreb’s cycle 32 or 34 38 2 6 2 2 2 3 Structure Your Knowledge Process Glycolysis Main Function Oxidation of glucose to pyruvate, 2 ATP net Inputs Glucose Pyruvate to acetyl CoA Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, which then enters Krebs cycle 2 pyruvate Kreb’s cycle Acetate from acetyl CoA is combined with oxaloacetate to produce citrate, which is cycled back to oxaloacetate as redox reactions produce NADH andFADH2, ATP is formed by substrate-level phosphorylation, and CO2 is released NADH (from glycolysis and Kreb’s) and FADH2 (from Kreb’s) transfer electrons to carrier molecules in mitochondrial membrane. In a series of redox reactions, H+ is pumped into intermembrane space, and electrons are delivered to 1/2O2 . The proton gradient drives H+ through ATP synthase to make ATP 2 acetyl CoA 10 NADH 2 FADH2 oxygen 10 NAD+ 2 FAD H2O 34 ATP Anaerobic respiration: glycolysis followed by regenteration of NAD+ so glycolysis can continue. Pyruvate is either reduced to ethanol and CO2 or to lactate See glycolysis above 2 pyruvate 2 NADH 2 ATP 2 NAD+ 2 ethanol and 2 CO2 OR 2 lactate Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis Fermentation Outputs 2 pyruvate 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 acetyl CoA 2 CO2 2 NADH 4 CO2 2 ATP 6 NADH 2 FADH2 4