* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Inheritance - Gaiser Middle School
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
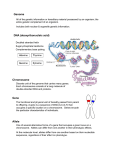
Human Inheritance Gaiser Life Science Know Human Inheritance What are some traits a child may share with one or both parents? Explain your answer. Evidence After listening to the PowerPoint lecture, come back here and list evidence to explain why your answer to the above question is or is not a good answer. You may also use other outside sources to help you respond. Page 43 Clarifying ?s Human Inheritance Information multiple alleles - a single gene that has more than two alleles or outcomes single gene - a trait controlled by 2 alleles How does environment affect genes? 1. diet – Lack of proteins, minerals, and vitamins can prevent a person from growing to full height. 2. living conditions – Better housing reduces infections and diseases. How many pairs? Example: three blood types A, B, & O Example: height at least 4 alleles Example: widow’s peak, white forelock 23 pairs of chromosomes in each human body cell Female sex chromosome pair = XX Male sex chromosomes = XY Page 44 Clarifying ?s Human Inheritance Information sex-linked genes - genes on the X and Y chromosomes - pass from parent to child Sex-linked traits - traits controlled by sex-linked genes carrier FYI Example: color blindness, muscular dystrophy - a person who has one recessive and one dominant allele for a trait They don’t have the physical trait, but they can pass the trait to their offspring. A carrier can carry a regular trait OR a sex-linked trait. Only females are sex-linked trait carriers. Males will display the physical trait if they receive it from their mother because the correct matching information for that trait does not occur on the reduced Y chromosome they received from their father. On the other hand, females who receive the sex-linked trait from their mother are more likely to have the correct matching information on the X chromosome they received from their father. This is why color blindness occurs in approximately 8% of males and only about 0.4% of females. Summary: Page 45 Clarifying ?s multiple alleles single gene How does environment affect genes? How many pairs? Human Inheritance Information Example: three blood types A, B, & O Example: height at least 4 alleles Example: widow’s peak, white forelock 1. diet – Lack of proteins, minerals, and vitamins can prevent a person from growing to full height. 2. living conditions – Better housing reduces infections and diseases. 23 pairs of chromosomes in each human body cell Female sex chromosome pair = XX Male sex chromosomes = XY Page 44 Clarifying ?s Human Inheritance Information sex-linked genes - genes on the X and Y chromosomes - pass from parent to child Sex-linked traits - traits controlled by sex-linked genes carrier FYI Example: color blindness, muscular dystrophy - a person who has one recessive and one dominant allele for a trait They don’t have the physical trait, but they can pass the trait to their offspring. A carrier can carry a regular trait OR a sex-linked trait. Only females are sex-linked trait carriers. Males will display the physical trait if they receive it from their mother because the correct matching information for that trait does not occur on the reduced Y chromosome they received from their father. On the other hand, females who receive the sex-linked trait from their mother are more likely to have the correct matching information on the X chromosome they received from their father. This is why color blindness occurs in approximately 8% of males and only about 0.4% of females. Summary: Page 45 This PowerPoint was created from Charlene Shea’s lecture notes by Tim Paterek. It is copyrighted and may not be reproduced outside the Vancouver School District. All pictures came from Google Image Search. To fall within the Fair Use Guidelines, this PowerPoint must be used within the confines of the classroom and may not be published back onto the Internet unless the pictures are removed.