* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concept 2: Living things inherit TRAITS in PATTERNS* We can
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
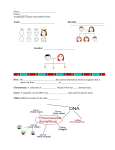
Concept 2: Living things inherit TRAITS in PATTERNS… We can PREDICT Traits! Review: Observe the Family Below and list some observable TRAITS What traits seem to have been passed down? Traits Review • Some traits are inherited ▫ Similar to the traits your parents have Eye color Hair color Height Number of arms • Some traits are acquired ▫ These traits your develop over your lifetime Athletic ability Reading and writing Language Review: Traits are coded by GENES • Genes are made out of DNA • Genes are located on your chromosomes ▫ You (human) contain 23 pairs of chromosomes (homologs). • Individuals inherit genes from their parents • Half of your genetic material is from your mom and half is from your dad. ▫ Crossing over during meiosis leads to genetic variation. Traits are Controlled by Interactions of Genes • Each homolog (pair of chromosomes) contains sites where genes are located. • The gene will be present on both of the chromosome pairs, however the form of the gene may be different • Different forms of the same gene are called alleles The Father of Genetics • Gregor Mendel performed the first major experiments investigating heredity (how genes are passed on) • University trained in Mathematics and Science • Experimented between 1856-1863 • Investigated inheritance among pea plants in his monastery’s garden Mendel’s Experiment • Observed eight different traits of pea plants: •Plant height •Seed shape •Pod shape •Flower postion •Pod postion •Seed color •Flower color •Pod color • Using one trait at a time, Mendel crossed two plants who were opposite forms of the same trait • Example: Trait – plant height ▫ Tall plant vs. a dwarf plant Mendel’s Conclusions • Each plant must have two “factors” for each possible trait, one factor from each parent • Some forms of a trait can be masked • Traits able to be masked can only be seen if both the plant’s factors are for that form of the trait • Mendel’s “factors” are now known as genes and alleles Genetic Terms • Phenotype describes the physical characteristic that is displayed by your genes; observable (eye color, hair color) • Genotype describes the actual genes that you have on your DNA; not always obvious (increased risk of Breast Cancer) Two Forms of Every Gene • Mendel found that your have two copies of each allele (one from your dad and one from your mom). • Alleles can be Dominant or Recessive ▫ Dominant Allele Always expressed as a capitol letter (T) Physically expressed, regardless of the other allele it is paired with (Tt or TT) ▫ Recessive Allele Physically expressed only when paired with another recessive allele (tt) Always expressed in a lowercase letter (t) Take Away Messages • The interactions of the alleles determines the phenotype of a certain trait. • Mendel found that there are two factors that come together when determining traits (one gene from your mom and one from your dad). • Alleles can either be recessive or dominant. ▫ In order for a recessive trait to be observed, there must be TWO copies of that recessive allele. ▫ In order for a dominant trait to be observed, there must be ONE dominant allele present.