* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inheritance of Traits
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
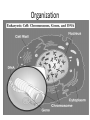
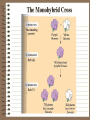
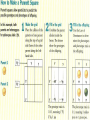
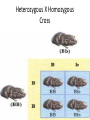
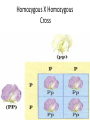
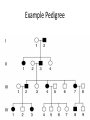
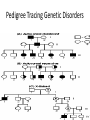
Genetics Vocabulary • Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to offspring • Gene- a section on a chromosome that has genetic information for one trait • Allele- different forms of a gene • Traits- genetic factors • Chromosomes-threadlike structures in the nucleus that contain genetic information that controls traits • DNA- an organism’s genetic material • Dominant trait-genetic factor that blocks another genetic factor • Recessive trait-genetic factor that is blocked by a dominant factor • F1 Generation- first generation offspring • P Generation- parent generation • Genotype- alleles that control a phenotype • Phenotype- how a trait appears • Every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits. This hereditary information (DNA) contains genes located in the chromosomes of each cell. Heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. Organization Mendel and Laws of Heredity • Gregor Mendel was the first to carry out studies of heredity • He studied height, flower color, seed coat color • He chose 1-2 traits per generation to watch • He crossed plants with different traits and learned that offspring usually had a dominant trait Mendel’s Discovery • He found that the inheritance of traits was not due to blending but instead specific traits or units of inheritance were passed from generation to generation • Those units are called inheritance genes Mendel’s Discovery cont. • The second generation would show a ratio of 3 to 1 • He deduced the presence of genes and alleles • Homozygous = same allele • Heterozygous = different allele Rule of Dominance • Similar genes are arranged in a similar order in a chromosome, the location on the chromosome is called a locus • Since 2 alternate forms are present we describe them as follows –Capital letters = dominant genes –Lower case letter = recessive genes • In a heterozygous pair, a dominant allele masks the presence of a recessive allele Punnett Squares • Punnett squares were devised as a short-hand way of finding expected outcomes of a cross • Punnett squares can be used for monohybrid crosses or dihybrid crosses • Each parent has 2 alleles for each trait • When gametes are produces, 50% have 1 allele for the trait and 50% have the other Heterozygous X Heterozygous Cross Heterozygous X Homozygous Cross Homozygous X Homozygous Cross Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics • Mendel’s theories can be used to explain how human traits are passed from one generation to the next • Pedigrees are used to show the passing of traits in humans Pedigree Symbols Example Pedigree Pedigree Tracing Genetic Disorders