* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infectious Diseases PPT
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
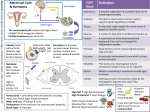
We are surrounded by millions of… MICROBES Tiny organisms, such as bacteria and viruses, that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Microbes AKA MICROORGANISMS oFound on all surfaces of things you touch oIn the air you breathe oAll surfaces of your body MICROBES Microbes can be POSITIVE: o Decompose waste o Make nutrients Most microbes are harmless! Others… develop infectious diseases WHAT IS AN INFECTIOUS DISEASE? Diseases caused and transmitted from person to person by microorganisms or their toxins Also referred to as: o Communicable/Contagious diseases o Infections PATHOGENS Microbes that cause disease 1. Bacteria 2. Virus Microscopic single celled organism capable of causing disease. Organisms that contain only genetic material and protein coats, and that are totally dependent on the cells they infect. BACTERIA o Bacteria thrives in warm, dark, moist environments o Example: Deep puncture wounds o A weakened immune system will result in illness if bacteria is present Beneficial Bacteria! o Digestive tract Tetanus Shot BACTERIA VS. VIRUSES: WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE Bacteria Independent single cell organisms Viruses Completely dependent on cells within the human host GENETIC MATERIAL VIRUSES Using the human host cells, viruses tap into the genetic code of the cells, and use the cell to reproduce more of the virus New viruses will continue to circulate throughout the human host and infect other healthy cells Parasitic Relationship VIRUSES o It is typical for people to suffer through one cold, or upper respiratory tract infection in a year – once symptoms subside, the virus is usually gone from the body o Some viruses can remain in the body long after symptoms diminish – these viruses are still communicable DORMANCY OTHER HARMFUL PATHOGENS 1) Fungi – living things that absorb and use nutrients of organisms they invade 2) Protozoa – tiny, animal like cells, some of which can cause illness 3) Worms – visible parasites that burrow into the blood supplies of victims 4) Parasites – living things that depend on the bodies of others that they inhabit HOW CAN WE DEFEND AGAINST INFECTIOUS DISEASES Our immune system is our bodies natural defense against illness and disease…as we age our immune system adapts HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD? Example: o Someone who has a cold may sneeze into the air, bacteria will circulate and land on various surfaces o Another person breathes in the bacteria, touches an object that was infected and catches the cold o The cycle repeats – continually spreading and contracting of illness 1) HOW ARE PATHOGENS CONTROLLED? Disinfectants – chemicals that kill pathogens on surfaces 2) Washing hands with soap and warm water, regularly 3) Treating open wounds with antiseptic ointment and properly covering the wound 4) Public sanitation – water treatment plants CONTROLLING INFECTIOUS DISEASES Vaccines : drugs made from alter microbes or their poisons injected or given by mouth to produce immunity Public health organizations control diseases but cannot eliminate them! THE BODY’S DEFENSE Natural barrier against infectious diseases: Skin, Membranes Immune system can block most infectious diseases IMMUNE SYSTEM Bone marrow produces lymphocytes (white blood cells) – imperative in immunity! Thymus gland transforms lymphocytes -> T cells Other lymphocytes become B cells = antibodies Protein molecules that fight infectious invaders IMMUNE SYSTEM Antigens Foreign substances in the body (bacteria/viruses) that stimulate the immune system and produce antibodies. IMMUNE SYSTEM During periods of infection: o Lymphocytes draw back into the lymph nodes – causes swelling o Travel through body fluids when adequately prepared to fight o Histamine inflammation of tissue o Inflames site of attack and draws defenders to aid in that location o Antihistamines are taken to reverse the effects and relieve unwanted symptoms IMMUNE SYSTEM T and B cells work as a unit T cells detect an enemy and send out chemical messages B cells respond to the message by making antibodies that destroy the pathogen Remaining lymphocytes “remember” the invader so that in the future, the illness will not occur or be nearly as detrimental COURSE OF AN ILLNESS Bacterial Infection: o Antibiotics can be utilized o Specific antibiotics must be used for specific pathogens Viruses are not cells! Viral Infections: o Antibiotics CANNOT be utilized o Why? – antibiotics prevent cell growth o Viruses must run its course – basic medicines can be used to relieve symptoms COURSE OF AN ILLNESS o Body’s natural reaction to infection = FEVER o Assist the body in fighting an infection by increasing temperature and making the environment unsuitable for the infection to thrive in o Activates the immune system TAKING ACTION o o o o o Keep immunizations current Eat a healthy diet Reduce or eliminate alcohol intake Reduce and manage stress Get regular exercise AIRBORNE INFECTION o o o o Cover your face when you sneeze and cough Avoid touching contaminated surfaces Bathe regularly Always wash your hands with soap and water – especially when handling food FOOD SAFETY Bacteria in foods can cause infection/poison in the digestive tract – prepare food correctly