* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic molecules
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
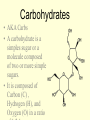
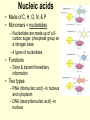
1/14/09 Warm-up: Convince me that you are alive. You must have ALL of the 8 criteria for life. Write each of them down and check them off to be sure that you are, indeed, living! The four major biomolecules Organic molecules part 1 What are we going to learn? SB1.c Identify the function of the four major macromolecules (i.e. carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids). ATOMS ATOMS • Building blocks of matter • teeny tiny!- billions can fit on the head of a pin • Made up of protons, neutrons & electrons ELEMENTS – Made up of one type of atom Ex. O, H, Fe -anybody know what these symbols represent? – Elements of Life • 96% Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), and Nitrogen (N) COMPOUNDS • Formed when elements combine ex. CO2, NaCl MOLECULE • Compound held together by covalent bonds (shared) ex. H2O Organic vs. Inorganic • All compounds can be separated into two groups: – Inorganic • Doesn’t contain carbon • Non-living • Examples: Oxygen gas, metals, rocks, water – Organic • Contains carbon • Living (or dead) • Examples: wood, grass, petroleum Organic Chemistry • Carbon: very versatile **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins More Must Knows! • Monomers: one unit of a compound -smaller, simple molecule that can join together to form larger molecule Mono = single; mer = part • Polymers: many monomers combined -complex molecule formed when 2 or more monomers combine poly = many • Macromolecules -Many large molecules combined -Formed by polymerization - carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins Biomolecules • They are the foundation for the structure and function of every living cell in every organism. • They are the building materials and the storehouse for energy. Carbohydrates • AKA Carbs • A carbohydrate is a simples sugar or a molecule composed of two or more simple sugars. • It is composed of Carbon (C) , Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O) in a ratio More than one class... • Monosaccharides are a single sugar molecule. An example is glucose. More than one class .... • Polysaccharides are long straight or branched chains of hundreds even thousands of sugar molecules in length. -examples: starch, cellulose Lipids • Organic molecules that have more carbon-hydrogen (CH) bonds and fewer oxygen atom than carbohydrates. • Commonly called fats, oils and waxes. • Lipids do not dissolve in water due to the nonpolarity of the lipid molecules. So you need a little bit of soap What? We want fats? • Used for long term energy storage, insulation, and protective coatings. • Major component of plasma membranes. And so do plants? • Waxes are long chains of fatty acids attached to an alcohol. Cutin is a wax that helps plants retain water. • Monomers of Lipids are fatty acids: -saturated fats = butter (main cause of high blood pressure) -trans fats = margarine, beef, pork (raise cholesterol levels) -unsaturated fats = nuts, olive oil -polyunsaturated fats = fish, cooking oils (may help lower cholesterol) Which type is best for you? worst? Proteins • Large complex polymers • They are composed of amino acids made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. • Monomers are amino acids – There are 20 different amino acids that combine in different ways to make millions of proteins – Carboxy group (-COOH) & amino group (NH2) – The most diverse macromolecule • Functions – – – – Control the rates of chemical reactions (enzymes) Regulate cell processes Used to form bone & muscles Transport substances into or out of cells to help fight disease – Part of the cell plasma membrane • Examples: collagen, enzymes, hemoglobin, insulin, and antibodies Nucleic acids • Made of C, H, O, N, & P • Monomers = nucleotides – Nucleotides are made up of a 5carbon sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogen base – 4 types of nucleotides • Functions – Store & transmit hereditary information • Two types – RNA (ribonucleic acid) –in nucleus and cytoplasm – DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) –in nucleus Nucleotides are pretty useful... • Are the structural units of adenosine phosphates (ATP, NAD+, NADP+), nucleotide coenzymes, and nucleic acids (DNA, RNA)