* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
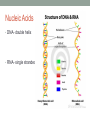
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Carbon: the element of life Important Terms to Know • Organic molecule: anything containing carbon • Carbon is an essential molecule in all living things • Can make up to 4 bonds with other atoms- versatile • Monomer: a single unit • Polymer: a structure made of many single units, or monomers • Example: a beaded necklace • The beads are all monomers • The necklace, put together, is a polymer. Carbohydrates • Carbohydrate monomers are called monosaccharides • Monomer examples • Glucose (C6H1206) • Galactose (C6H1206) • Fructose (C6H1206) • General Structure of the monomera ring Carbohydrates • Functions • Provide short term energy to an organism • Provides structure to cell walls (cellulose) • Polymers Name of polymer Function Cellulose Structure for plant cell walls Starch Energy storage for plants, in vacuole Glycogen Energy storage in animals, in liver and muscles Carbohydrates Fun Facts • The human body can not digest cellulose! • Anyone want to provide evidence for this? Lipids • Lipids are also known as fats • Monomers are made of (there are no polymers): 1. A glycerol 2. At least one fatty acid tail • Examples of lipids are: monoglyceride, triglyceride, saturated fat, unsaturated fat • General Structure Lipids • Functions • Provide long term energy to an organism • Provides structure of cell membranes (phospholipids) • Insulation • Saturated vs. Unsaturated fats • Saturated fats have hydrogens at every possible spot (solids) • Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond (liquids) Lipids Fun Facts Proteins • Protein monomers are called amino acids • Monomer examples- there are 20 different amino acids • Valine, tryptophan, serine • General Structure of the monomer- Proteins • Functions (just a few- there are MANY!) • Make up muscle • Make reactions happen faster (catalyst)- ENZYMES • Make antibodies to help you fight infections- ANTIBODIES • Polymers look like this: • they are HUGE and very complex Nucleic Acids • Nucleic acid monomers are called nucleotides • Monomers (nucleotides) are made up of 1. Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, G- or U in RNA) 2. Phosphate group 3. 5 carbon sugar (either deoxyribose-DNA or ribose-RNA) • General Structure of the monomer- Nucleic Acids • Functions • Code of life • Central dogma of biology: DNA RNA Protein - - Traits • Polymers Name of polymer Function DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) Permanent code for all traits RNA (ribonucleic acid) Disposable copy of genescode for a protein Nucleic Acids • DNA- double helix • RNA- single stranded Foods? • What foods that you eat contain each of these 4 organic molecules? • Carbohydrates? • Lipids? • Proteins? • Nucleic Acids?